Tabla de contenido
Palanca1. Introducción
Running wires in a building is a lot like laying out a roadmap—you need safe, protected pathways that can twist, turn, and fit around obstacles.
That’s exactly what flexible conduit does. It protects electrical wiring while bending easily around tight corners, making it an essential part of modern electrical systems in homes, businesses, and industrial spaces.
In this post, we’ll break down the main types of flexible conduit, how each one works, where they’re used, and what to consider when choosing the right type for your project.
Whether you’re a contractor, electrician, engineer, or just someone working on a home upgrade, this guide will help you understand how to use flexible conduit safely and effectively.
2. What Is Flexible Conduit?
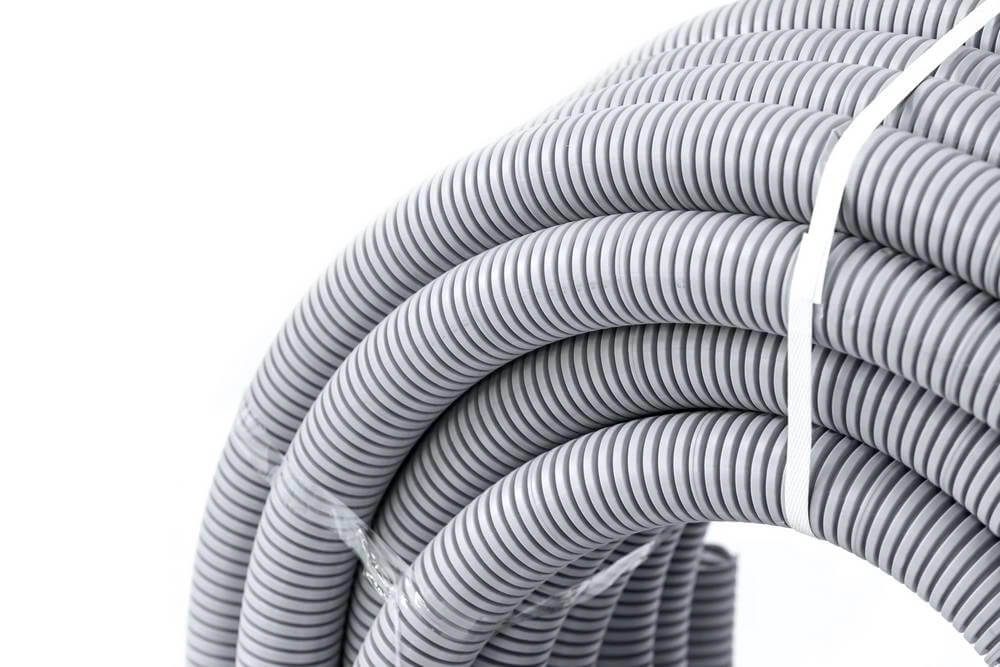
Most flexible conduits have a corrugated, ribbed outer surface, which gives them extra flexibility and strength.
Some types have a smooth outer jacket, especially when liquid-tight protection is needed. Internally, flexible conduit can be made from a single material (like PVC or metal), or as a composite, with a metal core wrapped in a non-metallic jacket—often used for harsh environments where both durability and sealing are required.
Flexible conduits come in a variety of colors, which may indicate their use (e.g., gray and orange for general electrical, white for communications, blue for data). They’re also manufactured to meet different national standards, such as UL listed, CSA certified, IEC and AS/NZS 2053 Standard and so on.
Choosing the right flexible conduit means understanding not only its shape and flexibility, but also the materials, performance ratings, and regulatory compliance that apply to your specific project or region.
In the following sections, we’ll walk through the most common types of flexible conduit, exploring their structure, key features, and where they’re best used.
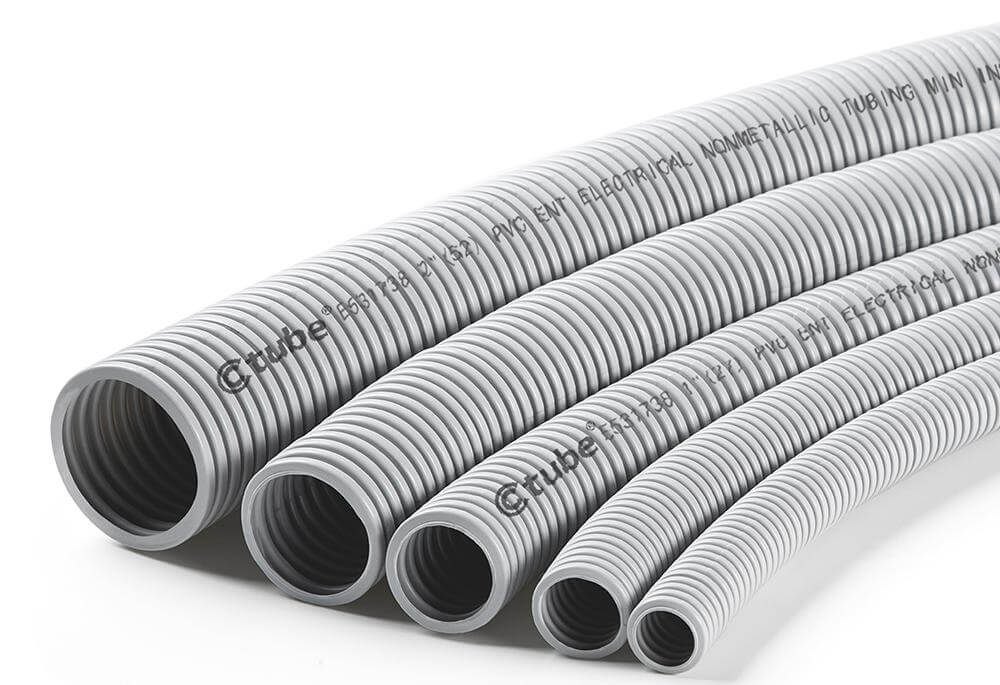
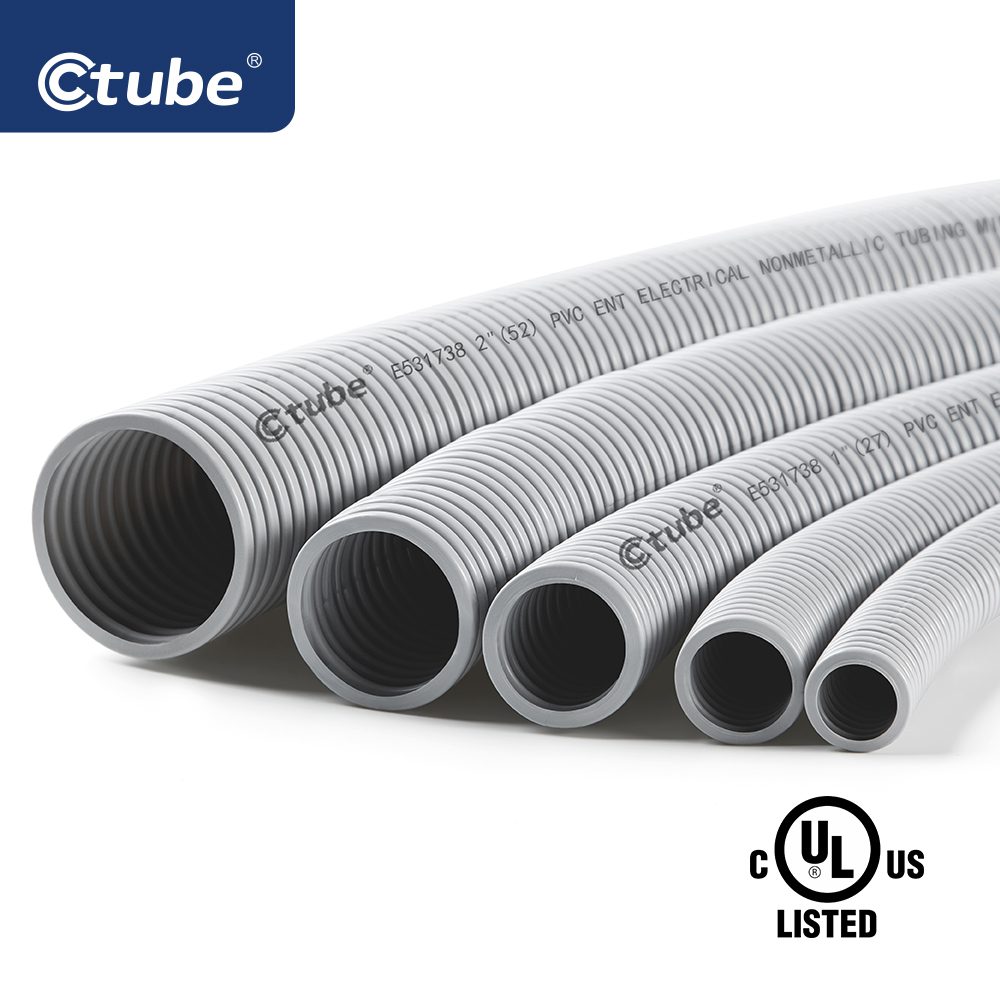
3. ENT Flexible Conduit: Lightweight Tubing with Hidden Strength
🧱 Structure and Manufacturing
ENT is extruded from modified polyvinyl chloride (PVC) with built-in flame retardants and stabilizers. What makes ENT unique is its corrugated wall structure, which offers directional flexibility while maintaining crush resistance. It’s engineered with memory—meaning it flexes without kinking and returns to its original shape when released.
Unlike smooth-wall PVC conduit (like Schedule 40 or 80), ENT is not intended for outdoor use or areas exposed to direct sunlight, unless specifically listed for that purpose. It also differs from flexible metal conduit in that it’s non-metallic and non-conductive, making it safer to use around combustible building materials or in situations where galvanic corrosion is a concern.
🔌 Electrical Performance and Wire Pulling
One often overlooked advantage of ENT is its low coefficient of friction, which allows easier wire pulling—especially around long, curved runs. ENT is typically installed empty, and wires are pulled after the tubing is secured, reducing the risk of insulation damage during installation.
ENT is compatible with THHN, THWN, or low-voltage cables, and due to its tight bend radius, it can often reduce the need for elbows and junctions. However, its internal diameter can vary slightly due to the corrugation, so pulling tension limits and conductor fill should always be double-checked per code.
🧩 System Integration and Fittings
ENT is part of a full wiring system and works best when used with matching solvent-weld or mechanical fittings (e.g., snap-in couplings, ENT-specific boxes). These fittings are designed to maintain fire ratings in slab or wall systems. In fire-rated assemblies (such as concrete floor slabs).
📘 Standards and Regulations
ENT se fabrica e instala de acuerdo con normas y regulaciones específicas para garantizar su seguridad y compatibilidad.
In the United States, the National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines for the installation of ENT, specifying the appropriate methods for its use and the types of applications it is suitable for.
UL1653 states the safety and mechanical performance for it, including its fire resistant performance, bending, resistance to deflection, impact, tension, stiffness.
En Canadá, el ENT debe cumplir con el estándar local CSA C22.2 No.227.1, este estándar indica la seguridad y el rendimiento del ENT, comparte el mismo método de prueba con UL1653.
Los códigos eléctricos locales también pueden tener requisitos específicos, por lo que es importante consultar las normas y regulaciones pertinentes para su región.
4. How to Install Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing
When installing ENT, it is important to follow proper guidelines to ensure a safe and effective installation.
Planning: Determine the appropriate size and length of ENT needed for the installation. Consider factors such as the number of wires, the route of the conduit, and the specific requirements of the project.
💡 If you want to know more about electrical nonmetallic tubing ENT, you can read this post: The Ultimate Guide to Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (ENT): Everything You Need to Know.
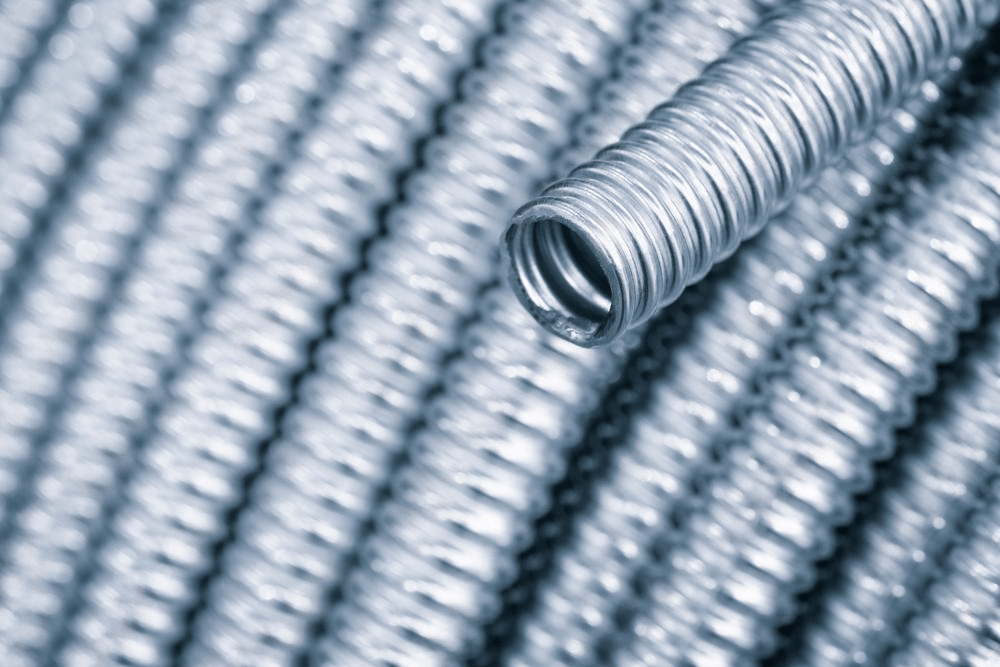
5. FMC Flexible Metal Conduit: Durability and Flexibility in One Coil
Flexible Metal Conduit (FMC) is a helically wound, interlocking metal conduit designed for applications that demand both mechanical protection and flexibility. It’s often described as the “go-to” choice when wiring needs to move with machinery or bend around structural obstacles—without sacrificing strength.
While ENT is known for its ease in low-risk environments, FMC is built for tougher conditions where abrasion resistance, EMI shielding, or grounding continuity are required.
⚙️ Mechanical Construction: Spiral Strength
FMC is made from a continuous strip of galvanized steel or aluminum, cold-formed into a spiral interlocking profile. This design allows for:
🔌 Grounding and Electrical Characteristics
One critical functional benefit of FMC is that the metal conduit itself can serve as the equipment grounding conductor (EGC)—provided the connections are tight and approved for grounding use (NEC 250.118(5)). This simplifies wiring in certain commercial or retrofit applications.
Additionally, because it’s a metal body, FMC offers some natural EMI shielding, making it useful in environments with interference-sensitive electronics—though it’s not rated the same as purpose-built shielded systems.
FMC is used with type THHN, THWN, XHHW conductors, and must be properly derated if subject to ambient heat.
6. How to Install Flexible Metal Conduit?
7. Liquid-tight Flexible Conduit: LFMC and LFNC
Liquid-tight Flexible Conduit is a type of flexible conduit that, as the name suggests, provides a liquid-tight seal around the wires it houses. It comes in two main types: LFMC and LFNC.
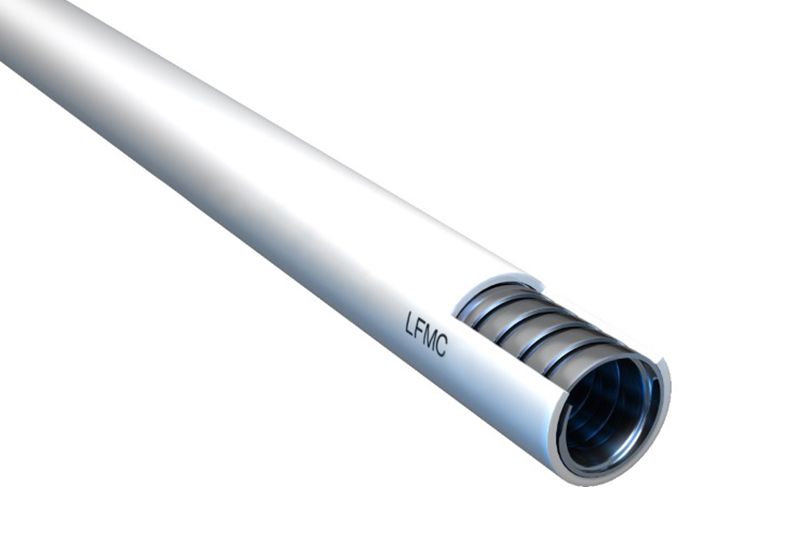
7. 1 LFMC: Liquid-Tight Flexible Metal Conduit for Harsh Environments
When electrical wiring needs both mechanical strength and protection from water, oil, or dust, LFMC (Liquid-Tight Flexible Metal Conduit) is the trusted choice. It’s built for environments where ordinary conduit would fail—such as machine rooms, rooftops, car washes, or outdoor lighting exposed to the elements.
🧱 Layered Construction for Maximum Protection
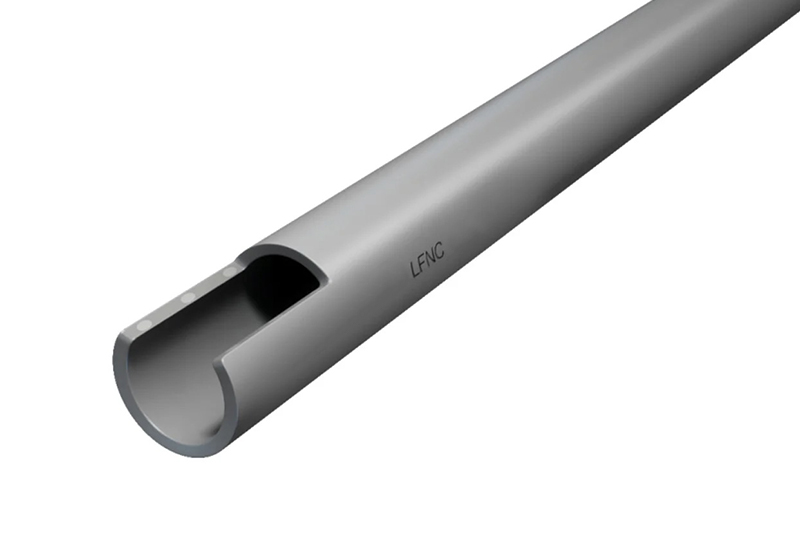
7.2 LFNC: Liquid-Tight Flexible Nonmetallic Conduit—Flexible, Corrosion-Resistant
LFNC (Liquid-Tight Flexible Nonmetallic Conduit) is the go-to choice when you need moisture and corrosion protection in non-metal-sensitive environments—and want to avoid the weight, cost, or grounding complexity of metal conduit. It’s especially useful in outdoor or damp applications where flexibility and ease of installation are just as important as durability.
Unlike LFMC, which uses a metal core wrapped in a jacket, LFNC is entirely non-metallic, typically made from PVC or other thermoplastic materials. That gives it unique advantages in terms of corrosion resistance, dielectric strength, and long-term flexibility.
🧱 Construction and Variants
8. HDPE Conduit: Flexible Protection for Long-Distance and Outdoor Use
Though not always grouped with traditional indoor wiring systems, HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) conduit is also a form of flexible conduit, especially valued for long-distance underground and outdoor installations. It offers exceptional tensile strength, impact resistance, and smooth inner walls, making it ideal for pulling fiber optics or power cables over extended distances with minimal friction.
Unlike PVC or LFMC, HDPE is heat-fused rather than glued or mechanically connected—making it seamless and watertight, but requiring specialized tools and techniques for joining.
We’ve covered this topic in more detail in another article. If you’re interested in the differences between HDPE and PVC conduit—including strength, flexibility, and installation methods—feel free to check out: PVC Conduit vs HDPE Conduit: What’s the Difference?
9. How to Choose the Right Flexible Conduit?
Choosing the right flexible conduit for your specific application requires considering several factors.
📘 Want a more detailed breakdown for outdoor environments? Check out our post Choosing the Right Flexible Electrical Conduit for Outdoor Use: A Comprehensive Guide
10. Conclusión
Flexible conduit plays a critical role in modern electrical systems by offering the versatility, protection, and ease of installation that rigid systems often can’t match. From lightweight ENT to rugged LFMC, from corrosion-resistant LFNC to infrastructure-grade HDPE, each type of conduit is engineered for a specific set of demands.
En Tubo C, we specialize in the development and manufacturing of high-quality PVC conduit systems—including a wide range of flexible conduit solutions. Our products are tested to meet international standards like UL, CSA, IEC, and are widely used across residential, commercial, and industrial installations.
Thank you for reading! We hope this guide is helpful. If you have questions, need product specs, or want to request samples, feel free to contact us.
Wishing you success with your next installation. Let the right conduit lead the way.