1. المقدمة
إذا سبق لك العمل في مشروع كابلات منظم أو استكشاف تركيب الألياف الضوئية أو الإيثرنت أو أنظمة الدوائر التلفزيونية المغلقة، فربما تكون قد صادفت مصطلح "قناة الاتصالات".“
بعض الناس على دراية به، لكنه لا يزال غامضًا بالنسبة للكثيرين. ما هو بالضبط قناة الاتصالات؟ هل هي مجرد نوع آخر من قنوات الكهرباء؟ هل هي نفسها قناة الألياف الضوئية؟ وكيف نختار القناة المناسبة؟
لست وحدك إن كنت تطرح هذه الأسئلة. قد يكون مصطلح "قناة الاتصال" مُربكاً لأنه يُستخدم في تقنيات وبيئات مختلفة.
في هذا المنشور، سنركز على قنوات الاتصال وسنستعرض المفاهيم الرئيسية وأنواع القنوات والمواد والمعايير واستراتيجيات الاختيار - خطوة بخطوة.
إذا كنت مدير مشروع أو مقاولًا أو مهندسًا، فقد تكون هذه المقالة مفيدة بشكل خاص في مساعدتك على اتخاذ قرارات مدروسة.
2. ما هي قناة الاتصال؟
قناة الاتصالات هي نوع من الأنابيب الواقية تُستخدم لتغليف وتوجيه كابلات الاتصالات ذات الجهد المنخفض. قد تشمل هذه الكابلات ما يلي:
كابلات الألياف الضوئية (لإنترنت عالي السرعة ونقل البيانات)
كابلات إيثرنت (Cat5e، Cat6، Cat6A لشبكات LAN)
كابلات محورية (للتلفزيون وكاميرات المراقبة)
كابلات إشارة منخفضة الجهد (لأجهزة الإنذار، وأجهزة الاتصال الداخلي، وأنظمة التشغيل الآلي)
3. ما هو الغرض من استخدام قناة الاتصال؟
الغرض من قناة الاتصال هو:
حماية الكابلات من التلف الميكانيكي والرطوبة والأشعة فوق البنفسجية
تنظيم وتبسيط تخطيطات الكابلات المعقدة
ضمان الامتثال لقوانين السلامة من الحرائق ولوائح البناء
ادعم التحديثات المستقبلية من خلال جعل الكابلات سهلة الوصول والاستبدال
على الرغم من تشابهها مع المواسير الكهربائية، إلا أن مواسير الاتصالات تستخدم عادة في التطبيقات غير المتعلقة بالطاقة، حيث تنقل الإشارات بدلاً من التيار الكهربائي.
اعتبرها بمثابة "الطريق السريع" الذي يحافظ على نظام الكابلات الهيكلية الخاص بك منظمًا وآمنًا وقابلًا للتوسع.
4. قناة الاتصال مقابل قناة الألياف الضوئية: ما الفرق؟
كما ذكرنا أعلاه، فإن إحدى الوظائف الرئيسية لقناة الاتصالات هي حماية كابلات الألياف الضوئية - والقناة المصممة خصيصًا لهذا الغرض، والمعروفة باسم قناة الألياف، هي في الواقع مجموعة فرعية من فئة قنوات الاتصالات الأوسع.
👉ببساطة، قناة الألياف هي نوع فرعي محدد من قنوات الاتصالات - مصممة لتلبية المتطلبات الفريدة لكابلات الألياف الضوئية، والتي تكون أكثر حساسية من الكابلات القائمة على النحاس.
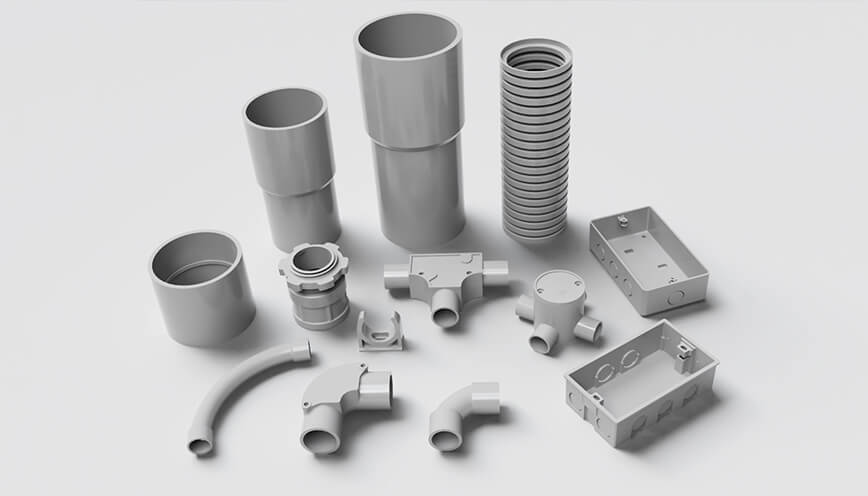
5. ما هي الأنواع الرئيسية لقنوات الاتصال؟
عند الحديث عن أنواع قنوات الاتصال، من المهم أن نفهم أنه لا توجد طريقة قياسية واحدة لتصنيفها - بدلاً من ذلك، يمكن تجميع قنوات الاتصال بناءً على المادة أو الهيكل أو بيئة التركيب أو التطبيق.
👀 دعونا نلقي نظرة فاحصة على أبعاد التصنيف الرئيسية الأربعة.
المادة ← البنية ← نوع الكابل ← بيئة التطبيق
5.1 تُصنف قنوات الاتصال حسب المادة لتناسب التطبيقات المختلفة
عند اختيار قناة اتصال، تحدد المادة خصائصها الميكانيكية ومقاومتها للحريق ومدى ملاءمتها للبيئة. تشمل الخيارات الشائعة ما يلي:
قناة اتصالات PVC—خفيف الوزن وسهل التركيب؛ ويستخدم عادة في الأماكن المغلقة أو في المناطق المحمية.
قناة من البولي إيثيلين عالي الكثافة—مرن ومثالي لتطبيقات الحفر تحت الأرض أو الحفر الموجه.
قناة اتصال LSZH—الأفضل للاستخدام في البيئات المغلقة أو ذات مستوى الأمان العالي مثل مراكز البيانات.
قناة معدنية (نادرة في مجال الاتصالات)—يستخدم حيثما تكون هناك حاجة إلى تعزيز الأمن أو الحماية.
أنابيب الألياف الزجاجية—قوي، غير قابل للتآكل، وغير معدني. مناسب للبيئات القاسية، بما في ذلك المواقع الخارجية أو الصناعية ذات درجات الحرارة العالية أو التعرض للمواد الكيميائية.
5.2 يمكن أن تكون قنوات الاتصال صلبة أو مرنة حسب متطلبات التصميم
يؤثر هيكل قناة الاتصال على كيفية ومكان تركيبها:
قناة اتصال صلبة—يوفر حماية مادية قوية؛ ويستخدم عادة في التطبيقات التجارية أو تطبيقات أنابيب الرفع.
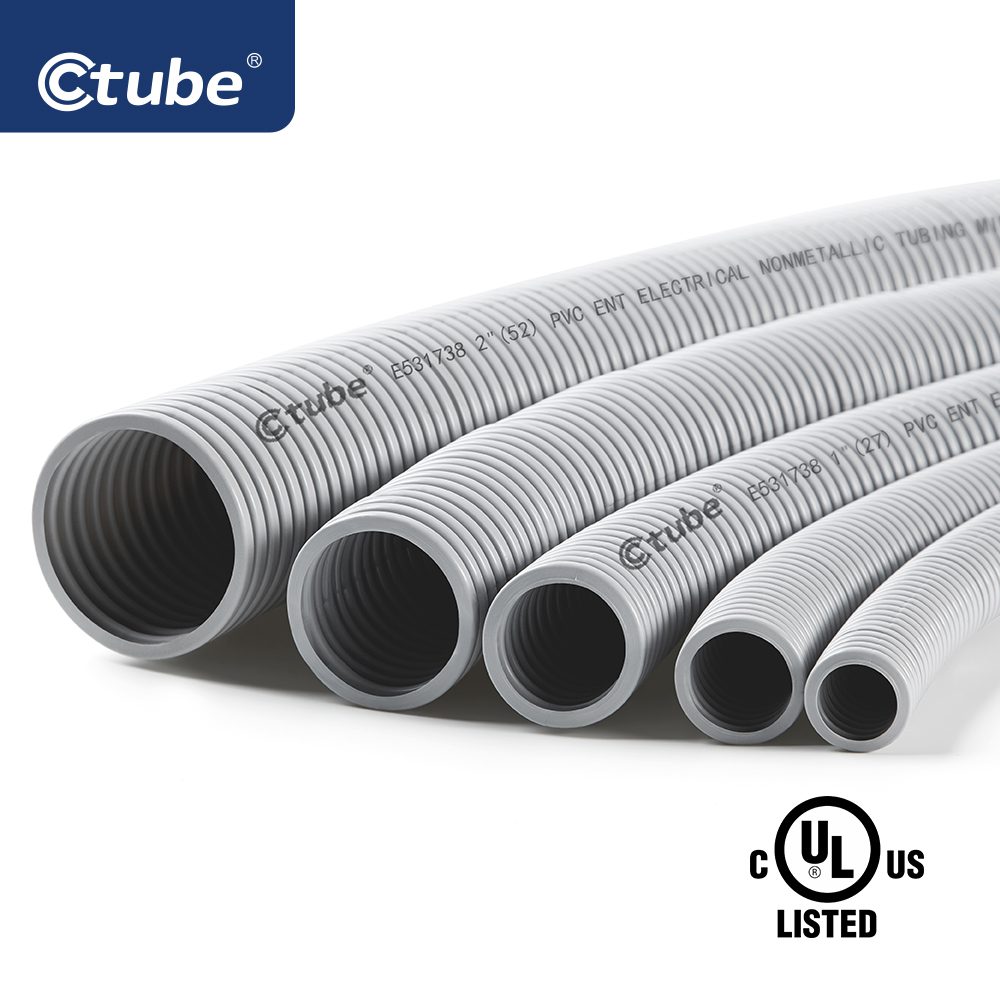
قناة اتصال مرنة—يوفر توجيهًا أسهل في البيئات الضيقة أو المعقدة.
5.3 يتم اختيار قنوات الاتصال بناءً على نوع الكابل الذي تحميه
ترتبط وظيفة قناة الاتصال ارتباطًا مباشرًا بنوع الإشارة أو الكابل الذي تحتوي عليه:
قناة كابلات الألياف الضوئية—مصممة لحماية كابلات الألياف الحساسة من الانحناءات أو الماء أو التلف الناتج عن السحق.
قناة إيثرنت لـ Cat5e/Cat6- يحافظ على سلامة الإشارة في شبكات LAN المنظمة.
قناة اتصال محورية—يدعم أنظمة الدوائر التلفزيونية المغلقة وأنظمة الترددات اللاسلكية من خلال حماية الكابلات الحساسة للحماية.
قناة اتصال هجينة— قنوات كبيرة تجمع أنواعًا متعددة من الكابلات لتركيبات الاتصالات المتكاملة.
5.4 يجب أن تتوافق قنوات الاتصال مع بيئة التركيب ومتطلبات الكود
تتطلب البيئات المختلفة تصنيفات مختلفة لقنوات الاتصال:
قناة اتصالات مصنفة للاستخدام في المساحات المفتوحة—يلبي معايير صارمة للحريق والدخان لأماكن معالجة الهواء (على سبيل المثال، UL 2024).
قناة اتصال مصنفة حسب الارتفاع—مناسب للتركيبات الرأسية بين طوابق المبنى.
قناة اتصالات تحت الأرض—مقاوم للرطوبة ومقاوم للسحق، وعادة ما يكون من البولي إيثيلين عالي الكثافة أو البولي فينيل كلوريد المصنف DB/EB.
قناة اتصال خارجية—مقاوم للأشعة فوق البنفسجية والظروف الجوية للتركيبات المكشوفة.
6. الاعتبارات الرئيسية لاختيار قناة اتصال
الآن وقد استكشفنا التصنيفات المختلفة لقنوات الاتصال، دعونا نخطو خطوة أخرى ونلقي نظرة على كيفية توجيه هذه التصنيفات لعملية اختيارك.
6.1 نوع الكابل ومتطلبات عرض النطاق الترددي
تختلف الاحتياجات المادية والأداء لأنواع كابلات الاتصالات المختلفة - مثل كابلات الألياف الضوئية، وكابلات Cat6، والكابلات المحورية، وكابلات الأزواج الملتوية.
فعلى سبيل المثال، تتطلب كابلات الألياف الضوئية قنوات ذات أسطح داخلية ملساء وأقطار واسعة بما يكفي لتجنب إجهاد الانحناء.
غالباً ما تحتاج التطبيقات ذات النطاق الترددي العالي إلى مساحة أكبر وعزل أفضل للتداخل الكهرومغناطيسي.
6.2 بيئة التركيب
هل يمر الأنبوب داخل المبنى، أم خارجه، أم تحت الأرض، أم في المساحات المفتوحة؟
تحتاج التركيبات الخارجية أو تحت الأرض إلى قنوات مقاومة للأشعة فوق البنفسجية ومقاومة للماء، مثل PVC أو HDPE.
6.3 مقاومة الحريق والحماية من التداخل الكهرومغناطيسي
تتطلب بعض التطبيقات مقاومة معززة للحريق وحماية من التداخل الكهرومغناطيسي (EMI).
استخدم قنوات اتصال معدنية أو طبقات حماية مركبة في المناطق المعرضة للتداخل الكهرومغناطيسي مثل مراكز البيانات أو المواقع الصناعية.
بالنسبة للمباني المعرضة للحريق، تعتبر الأنابيب الخالية من الهالوجين أو المصنفة للاستخدام في الأماكن المغلقة أمراً بالغ الأهمية.
6.4 تخطيط المساحات وقابلية التوسع المستقبلية
اختر أحجام الأنابيب التي تسمح بإضافة كابلات إضافية لاحقًا.
تساهم أنظمة المواسير المعيارية والوصلات وصناديق السحب في تسهيل عمليات التحديث والاستبدال.
6.5 الامتثال للمعايير المحلية والدولية
عند اختيار قناة اتصال، من المهم اتباع المعايير المحلية والدولية لضمان السلامة والتوافق والأداء على المدى الطويل.
في الولايات المتحدة، تنظم قوانين أساسية مثل معايير NEC وTIA استخدام قنوات الألياف الضوئية والكابلات المحورية وغيرها من كابلات الاتصالات. ابحث عن الخيارات المدرجة في قائمة UL لضمان السلامة.
في أستراليا ونيوزيلندا، توفر المعايير AS/NZS 2053 و AS/CA S009:2013 قواعد واضحة لنوع القناة ولونها وتركيبها - خاصة في الأماكن الخارجية وتحت الأرض.
على الصعيد العالمي، توجه معايير مثل ISO/IEC 14763-2 و EN 50085 استخدام المواسير في أنظمة الكابلات الهيكلية وأنظمة تكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات.
🌏يساعد اتباع هذه المعايير على ضمان أن يكون تركيبك آمنًا ومتوافقًا مع المعايير ومصممًا ليدوم طويلًا.
7. فهم ترميز الألوان والامتثال لأنظمة الاتصالات في أستراليا
استنادًا إلى التعليقات التي جمعناها من الكهربائيين والمهندسين والمقاولين - إلى جانب الإشارات إلى معايير الصناعة الرئيسية - وجدنا أنه في أستراليا ونيوزيلندا، فإن AS/NZS 2053 متوسط الخدمة أبيض غير معدني هو الأكثر شيوعًا في استخدام كابلات الاتصالات، مثل MD أبيض PVC مع 750 نيوتن.
هذا الخيار ليس عمليًا فحسب، بل يتوافق أيضًا مع عادات التركيب ومتطلبات الامتثال في كلا البلدين.
عند تركيب قنوات الاتصالات - وخاصة في بيئات مثل الأنظمة تحت الأرض أو الأنظمة الخارجية - يعد اللون والامتثال أمراً بالغ الأهمية للسلامة والوضوح.
المعايير الأسترالية مثل AS 1345:1995، AS/CA S008:2020 و AS/CA S009:2013 لقد قدموا إرشادات واضحة لسنوات.
سنقدم المحتوى المتعلق بالتواصل بين هذه المعايير واحداً تلو الآخر.
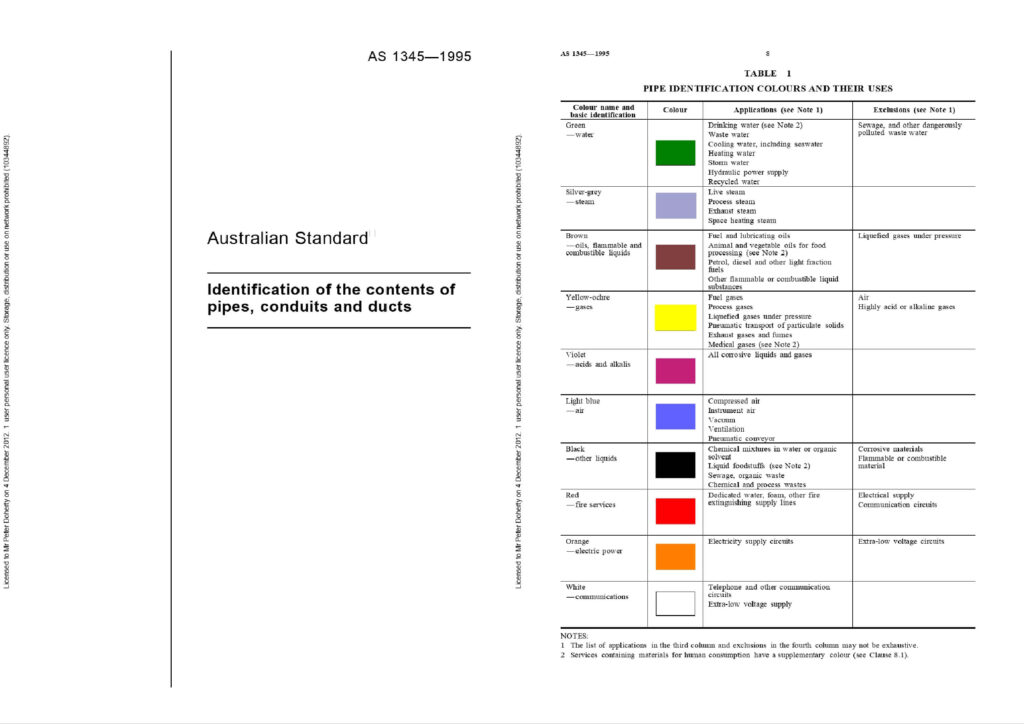
في أستراليا، يتم تحديد ألوان المواسير الكهربائية بموجب AS 1345:1995, ويجب ألا تستخدم قنوات الاتصال ألوانًا مخصصة للخدمات الخطرة.
وفق AS/CA S008:2020, إليكم متطلبات قناة الاتصالات تحت الأرض.
يجب أن تكون الأنابيب البلاستيكية تحت الأرض المستخدمة للاتصالات إما بيضاء بالكامل، أو تحتوي على شريط أبيض متين كجزء من عملية التصنيع (وليس مطليًا بعد ذلك).
يجب أن يكون الأنبوب متينًا ومقاومًا للرطوبة ومناسبًا للاستخدام المتوسط، سواء كان صلبًا أو مرنًا، قابلًا للربط أو غير قابل للربط، ومصنفًا وفقًا لمعيار IP66.
يجب وضع علامات واضحة ودائمة على القنوات تحت الأرض مكتوب عليها "الاتصالات" على فترات منتظمة، دون استخدام كلمة "كهربائي" لمنع حدوث لبس.
أثناء وجوده AS/CA S009:2013, هناك متطلبات أكثر تفصيلاً بشأن تركيب قنوات الاتصالات.
✅ نصيحة: اختر دائمًا ألوانًا غير مدرجة في هذه القائمة لأنابيب الاتصالات. الجدول التالي يوضح الألوان الخطرة التي يجب تجنبها في كابلات الاتصالات.
| لون | المعنى / الاستخدام |
| البرتقالي | التيار الكهربائي الرئيسي |
| أصفر | الوقود، والغازات السامة، والغازات الطبية |
| رمادي فضي | بخار |
| بني | السوائل القابلة للاشتعال أو الاحتراق |
| بنفسجي | الأحماض والقلويات |
| أزرق فاتح | الهواء المضغوط |
للاستخدام الداخلي، يُسمح بأي لون غير ضار، ولكن يُنصح باللون الأبيض للمساعدة في تجنب الالتباس.
كما ذكرنا أعلاه، يجب أن تكون قنوات الاتصال الخارجية بيضاء بالكامل أو تحتوي على شريط أبيض مدمج، ومميزة بوضوح بعبارة "الاتصالات"، ولا يمكن إعادة طلائها بألوان أخرى مثل البرتقالي لتلبية المعيار.
بالنسبة للتركيبات السطحية والهوائية الخارجية، يجب أن تكون كابلات الاتصالات مقاومة للأشعة فوق البنفسجية أو محمية بالكامل داخل قنوات مناسبة، وفقًا لمعايير AS/CA S008.
يجب تجنب الألوان الخطرة في قنوات الاتصالات تحت الأرض إلا إذا كانت مغلفة بالكامل بالخرسانة ومميزة باللون الأبيض، أو تم إدخالها في قناة متوافقة مع تصنيف IPX8، أو تم استخدامها لكابلات الألياف الضوئية مع تحذيرات ضوئية خطرة مناسبة.
عند تركيب الكابلات تحت الطرق أو الممرات، يجب دفنها في قناة متوافقة بعمق لا يقل عن 450 مم أو حمايتها بشريط تحذير أبيض عليه علامة موضوعة على بعد 100 مم على الأقل فوق الكابل.
8. فهم ترميز الألوان والامتثال لأنظمة الاتصالات في الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية
لا يوجد لدى NEC أي قواعد محددة بشأن ألوان المواسير، على عكس أستراليا ونيوزيلندا حيث توجد متطلبات واضحة.
لا يبدو أن هناك حاليًا أي معيار رسمي يحدد بدقة الألوان التي يجب استخدامها. بدلاً من ذلك، قام المقاولون والمهندسون بتطوير أنظمة ألوان عملية خاصة بهم لتسهيل التعرف على أنواع المواسير المختلفة.
بالنسبة لقنوات الاتصال، والتي تغطيها بشكل رئيسي المواد 770 و800 من قانون الكهرباء الوطني.
نقدم هنا بعض النقاط الرئيسية المطلوبة من المعيار.
كلاهما NEC 770 و 800 يجب التأكيد على ضرورة فصل قنوات وكابلات الاتصالات فعلياً عن خطوط الطاقة الكهربائية. يساعد ذلك على منع التداخل الكهرومغناطيسي والحفاظ على نقاء إشارات الاتصال.
يجب تأريض الأجزاء المعدنية لأنظمة الاتصالات، مثل المواسير وأغطية الكابلات، بشكل صحيح لتجنب المخاطر الكهربائية وتعزيز السلامة. يضمن هذا التأريض أن جميع الأجزاء المعدنية لها نفس الجهد الكهربائي، مما يحمي المعدات والأفراد.
ينبغي تركيب قنوات وكابلات الاتصالات بشكل أنيق ومنطقي.
تجنب الانحناءات الحادة أو المسارات المعقدة التي تُصعّب عمليات الإصلاح أو التحديث في المستقبل. يجب وضع الدعامات والمشابك على فترات منتظمة للحفاظ على استقرار المواسير وأمانها.
قد يؤدي ملء القنوات بشكل مفرط إلى ارتفاع درجة الحرارة أو تلف الكابلات، لذا يجب الالتزام بحدود الملء المناسبة. وبالنسبة لكابلات الألياف الضوئية تحديدًا (المادة 770)، يُعدّ حماية الكابلات داخل القنوات الداخلية أمرًا بالغ الأهمية لمنع التلف وتسهيل الصيانة المستقبلية.
تخضع كابلات الألياف الضوئية لمعايير أكثر صرامة لأنها حساسة للانحناء والإجهاد الميكانيكي. فهي تتطلب أقطارًا أكبر للأنابيب وانحناءات لطيفة لتجنب فقدان الإشارة أو تلف الكابل.
تُستخدم القنوات الداخلية عادةً لحماية كابلات الألياف الضوئية داخل الأنابيب. عند سحب كابلات الألياف الضوئية، يجب توخي الحذر لتجنب شدها أو ضغطها، لضمان استمرار موثوقية النظام على المدى الطويل.
يجب أن تستوفي كابلات وأنابيب الاتصالات معايير السلامة من الحرائق. على سبيل المثال، ينبغي إزالة الكابلات غير المستخدمة لتجنب مخاطر الحريق. لا يجوز تركيب الكابلات داخل الأنابيب التي تحمل الغبار أو الغازات أو المواد السائبة لأن ذلك قد يتسبب في تلفها أو مشاكل تتعلق بالسلامة.
في البيئات الخاصة مثل أماكن معالجة الهواء، يجب أن تستخدم الكابلات مواد مقاومة للحريق أو منخفضة الدخان لتقليل المخاطر أثناء الحريق.
9. الخاتمة
يُعدّ اختيار قنوات الاتصالات المناسبة أمرًا بالغ الأهمية للحفاظ على سلامة أنظمة الأسلاك وتنظيمها وجاهزيتها للمستقبل. سواءً كنت تخطط لتركيب إنترنت منزلي، أو نظام أمان تجاري، أو تركيب شبكة ألياف ضوئية واسعة النطاق، فمن المهم اتباع إرشادات أساسية عند اختيار القنوات. وهذا يعني مراعاة عوامل مثل البيئة، وحجم القناة، والترميز اللوني، والامتثال للمعايير المحلية.
ولدعم كل هذه الاحتياجات،, سي تيوب تقدم مجموعة كاملة من قنوات الاتصالات المصنوعة من مادة PVC والتي تلبي نحن. و المعايير الأسترالية. منتجاتنا متينة وخفيفة الوزن وسهلة التركيب، ومناسبة للاستخدام الداخلي والخارجي. سواء كنت بحاجة إلى قنوات لخطوط مدفونة، أو تركيبات جدارية، أو كابلات مراكز البيانات، فإن Ctube توفر حلولاً آمنة وموثوقة يمكنك الاعتماد عليها.
باستخدام القناة المناسبة، سيعمل نظام الاتصالات الخاص بك بشكل أفضل، وسيدوم لفترة أطول، وسيظل أكثر أمانًا.
📘 إذا كنت مهتمًا بمعرفة المزيد عن متطلبات مواسير التمديدات الكهربائية في معيار AS/NZS 2053، فراجع مقالتنا Uفهم معيار AS/NZS 2053: دليل شامل للمواسير الكهربائية.
🟠 إذا كنت مهتمًا بمعرفة المزيد عن أنابيب التوصيل الكهربائية البرتقالية، فلا تفوت كل ما يجب أن تعرفه عن أنابيب التوصيل الكهربائية البرتقالية.
🎯 هل ترغب في معرفة المزيد عن المواسير الكهربائية، ونصائح التركيب، وآخر مستجدات الصناعة؟
📩 تابعوا Ctube على لينكدإن أو وسائل التواصل الاجتماعي الأخرى مثل فيسبوك أو انستغرام أو يوتيوب, نحن نشارك بانتظام معلومات مفيدة حول أنابيب PVC والوصلات وأفضل الممارسات للمشاريع الكهربائية - سواء كنت مقاولًا أو مهندسًا أو تخطط لمشروعك التالي.
📚 اقرأ المزيد من المنشورات المفيدة من موقعنا صفحات المدونة لمعرفة المزيد عن المواسير الكهربائية.
شكرًا لكم على القراءة. نأمل أن يكون هذا المقال قد ساعدكم في اختيار المواسير المناسبة. إذا كانت لديكم أي استفسارات أو احتجتم إلى أي مساعدة إضافية، فلا تترددوا في التواصل معنا. نتمنى لكم التوفيق والنجاح في مشروعكم!