1. المقدمة
سواء كنت مقاولاً كهربائياً أو متدربًا جديدًا أو مدير مشروع أو حتى مالك منزل يعمل على الأسلاك الخاصة به، فإن معرفة كيفية استخدام جسم القناة يمكن أن يوفر لك الوقت والجهد والأخطاء.
❓ إذًا، ما هو بالضبط؟ جسم الموصل الكهربائي هو وصلة صغيرة مجوفة تربط الموصلات الكهربائية.
🔁 يتيح لك تغيير الاتجاه، وسحب الأسلاك بسهولة أكبر، والوصول إلى الأسلاك الخاصة بك لاحقًا للصيانة أو الفحص.
🧩 إنه جزء بسيط - لكنه مهم حقًا في أي نظام توصيل.
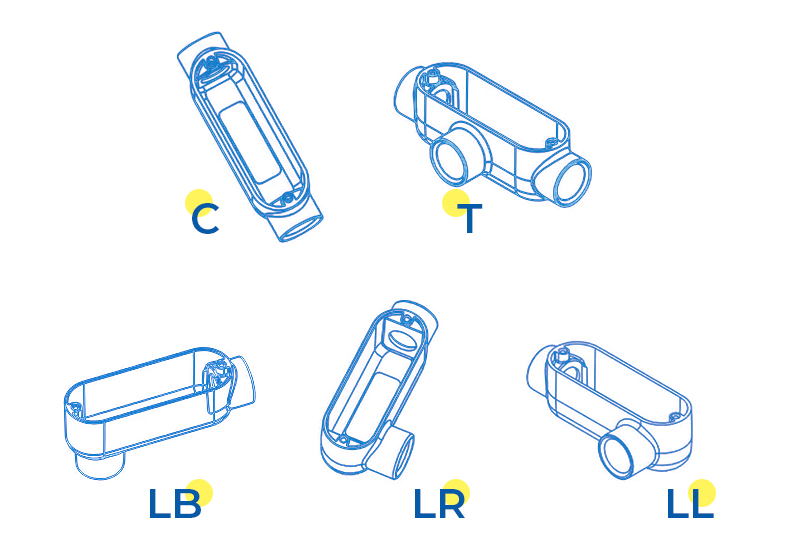
📦 هناك عدة أنواع - مثل LB وLL وLR وT وC - وكل منها يخدم غرضًا مختلفًا اعتمادًا على كيفية تخطيط القناة الخاصة بك.
📘 في هذا المنشور، سنلقي نظرة على ما تفعله أجسام القنوات، وكيف تعمل الأنواع المختلفة، وكيفية اختيار النوع المناسب، وما الذي يجب مراعاته عند تثبيتها.
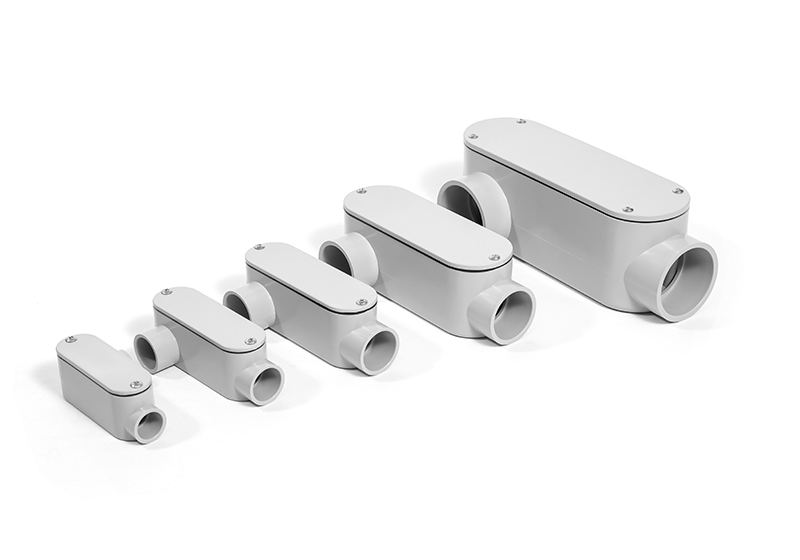
2. أفضل 6 أنواع من أجسام الأنابيب وكيفية استخدامها
دعونا نلقي نظرة على الأنواع الأكثر شيوعًا.
🔄 جسم قناة LB
يتوافق المدخل مع الغطاء، ويخرج المخرج من الخلف، ويشكلان انحناءة بزاوية 90 درجة.
هذا أحد أكثر أجسام الأنابيب استخدامًا. تدخل الأسلاك من الأمام وتخرج من الخلف، مما يجعلها مثالية للحالات التي ترتفع فيها الأنابيب من الجدار وتحتاج إلى الدخول إلى الجزء الخلفي من المبنى. غالبًا ما تُرى أجسام الأنابيب ذات القواطع المنخفضة بالقرب من قواعد العدادات أو مداخل الخدمات الخارجية.
↩️ جسم القناة LL
يتوافق المدخل مع الغطاء، ويخرج المخرج على الجانب الأيسر.
يسمح هيكل أنبوب التوصيل LL بدخول الأنبوب من أحد الأطراف والانعطاف يسارًا. وهو مفيد عند الحاجة إلى لف الأسلاك حول زاوية أو تمديدها يسارًا على طول جدار أو سقف. يتيح لك الغطاء سهولة الوصول إلى داخل المنحنى.
↪️ جسم قناة LR
يتوافق المدخل مع الغطاء، ويخرج المخرج على الجانب الأيمن.
مشابه لـ LL، لكن الانعطاف يكون إلى اليمين بدلاً من اليسار. استخدم هيكل LR عندما ينعطف تصميم القناة إلى اليمين، مثلاً حول زاوية جدار أو بين معدات على اليمين.
🛠️ جسم القناة T
تشكل محاور المدخل والمخرج خطًا مستقيمًا، مع وجود مخرج فرعي ثالث محاذي للغطاء (عادةً ما يكون عموديًا على المسار الرئيسي).
يشبه هيكل أنبوب التوصيل على شكل حرف T حرف "T". يتيح لك هذا الأنبوب تمرير الأسلاك بشكل مستقيم مع التفرع في اتجاه ثالث. يُعد هذا مفيدًا عند تقسيم أنبوب توصيل واحد إلى قسمين، على سبيل المثال، توجيه أحد الأنبوبين إلى المصابيح والآخر إلى المنافذ الكهربائية. عادةً ما يكون الغطاء مواجهًا للفرع، مما يُسهّل فحص الأسلاك أو سحبها من نقطة الوصل.
➖ جسم القناة C
المدخل والمخرج متوافقان مع بعضهما البعض - لا يوجد تغيير في الاتجاه.
هذا جسم أنبوب مستقيم يُستخدم غالبًا لسحب الأسلاك وفحصها. لا يتطلب أي دوران؛ فهو ببساطة يتيح لك الوصول إلى الأسلاك داخل مسار أنبوب مستقيم طويل. وهو عملي في المناطق التي يصعب فيها سحب الأسلاك بسبب المسافات الطويلة.
❌ جسم القناة X
تشكل محاور التوصيل الأربعة - الأمامية والخلفية واليسرى واليمنى - نمطًا متقاطعًا، مع وجود غطاء الوصول في المنتصف.
يشبه هيكل قناة X تقاطعًا رباعي الاتجاهات. يتيح لك توصيل القناة والوصول إليها في جميع الاتجاهات. على الرغم من أنه لا يُستخدم عادةً في الأعمال السكنية، إلا أنه يُستخدم أحيانًا في الأسقف التجارية أو التصميمات الصناعية حيث تلتقي خطوط قنوات متعددة. يُرجى العلم أن هذا النوع قد لا يُسمح به في كل مكان، لذا يُرجى مراجعة قانون منطقتك قبل استخدامه.
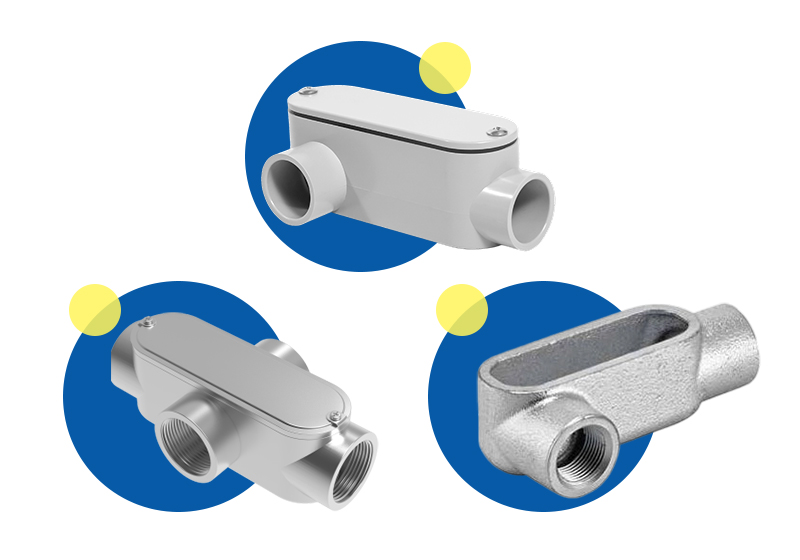
3. المواد الرئيسية والملاءمة البيئية
تُصنع هياكل الأنابيب من مواد أساسية قليلة، لكل منها خصائصها الخاصة، وتشطيب سطحها، وبيئة تطبيقها المثالية. أكثر الأنواع شيوعًا هي سبائك الألومنيوم، والفولاذ المجلفن، والـ PVC (غير المعدني).
أجسام الأنابيب المصنوعة من سبائك الألومنيوم
يُعدّ الألومنيوم مادةً شائعةً في صناعة هياكل الأنابيب نظرًا لخفة وزنه ومقاومته للتآكل وسهولة استخدامه. تُصنع معظم هياكل أنابيب الألومنيوم من سبائك الألومنيوم المصبوبة، مما يوفر متانة عالية مع الحفاظ على خفة وزن المنتج نسبيًا.
لتعزيز مقاومة التآكل، تُطلى العديد من هياكل أنابيب الألمنيوم بالمسحوق. يُخبز هذا الطلاء الجاف بالمسحوق لإنشاء سطح متين يحمي من الرطوبة والملح والمواد الكيميائية والأشعة فوق البنفسجية. تُناسب هياكل أنابيب الألمنيوم المطلية بالمسحوق التركيبات الخارجية والأماكن الرطبة والبيئات الساحلية. كما يمنح هذا الطلاء السطح مظهرًا أكثر نعومةً واحترافيةً - عادةً باللون الرمادي أو الأبيض.
قد تأتي بعض هياكل الألومنيوم بدون طلاء مسحوق. ورغم أنها لا تزال مقاومة للتآكل بفضل خصائص الألومنيوم، إلا أنها أكثر ملاءمة للاستخدام الداخلي أو البيئات الجافة، حيث يكون التعرض للعوامل الجوية القاسية محدودًا.
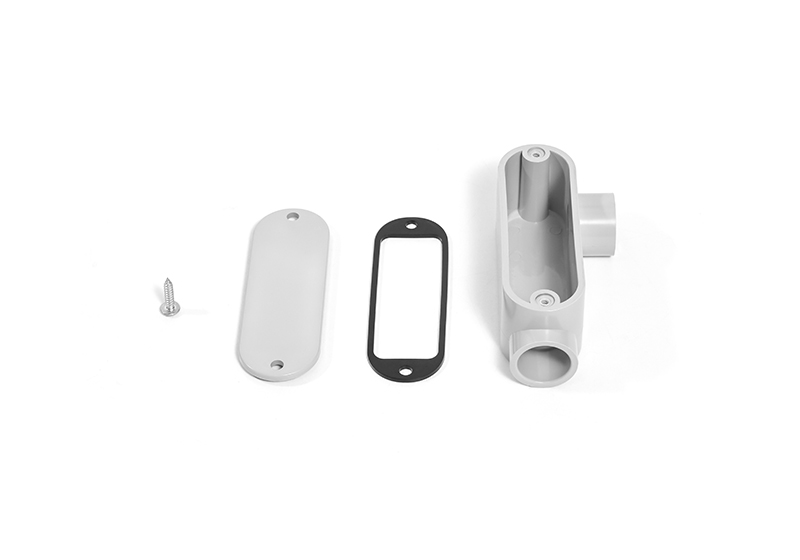
في كثير من الحالات، تتوفر هياكل أنابيب الألومنيوم مع أو بدون حشوات. توفر الأغطية المُحاطة حشوات إحكامًا محكمًا، مما يجعلها مثالية للأماكن الرطبة أو المبللة. تُستخدم الأنواع غير المُحاطة حشوات في التطبيقات العامة.
أجسام الأنابيب الفولاذية المجلفنة
تُصنع أجسام أنابيب الفولاذ المجلفن من الفولاذ المختوم أو المصبوب، مع إضافة طبقة من الزنك لمنع الصدأ. يُطبق هذا الطلاء الزنكي من خلال عملية الجلفنة بالغمس الساخن أو الطلاء الكهربائي. والنتيجة هي جسم متين ومقاوم للصدمات يتمتع بقوة ميكانيكية ممتازة.
بعض الهياكل الفولاذية مطلية أيضًا بمسحوق فوق طبقة الزنك، مما يوفر حماية مزدوجة. هذه الهياكل مناسبة للبيئات الصناعية، خاصةً حيث تكون القوة ومتانة السطح أمرًا بالغ الأهمية - مثل غرف الميكانيكا، ومصانع التصنيع، أو المناطق الخارجية المكشوفة.
تعتمد الهياكل الفولاذية غير المطلية بالمسحوق على طبقة الزنك فقط. يُفضل استخدامها في الأماكن المغلقة أو في المناطق الجافة، لأنها قد تصدأ في حال تلف طبقة الزنك في بيئة تآكلية.
تميل أجسام الأنابيب الفولاذية المجلفنة إلى أن تكون أثقل من الألومنيوم ويتم استخدامها بشكل أقل شيوعًا في البيئات التي يكون فيها التآكل مصدر قلق كبير.
أجسام الأنابيب البلاستيكية (غير المعدنية)
أجسام أنابيب PVC مصنوعة بالكامل من البلاستيك (بولي فينيل كلوريد)، وتوفر حلاً غير معدني وغير موصل للكهرباء. كما أنها مقاومة طبيعيًا للرطوبة والأحماض والقلويات ومعظم المواد الكيميائية.
تُستخدم هياكل أنابيب PVC عادةً في البيئات الرطبة أو المسببة للتآكل أو تحت الأرض، مثل مرافق معالجة المياه، ومصانع تجهيز الأغذية، أو بالقرب من المناطق الساحلية. ولأنها لا تصدأ، فهي مثالية في الأماكن التي يُخشى فيها تآكل المعادن.
عادةً ما يُغلق الجسم والغطاء بإحكام باستخدام حشوات أو وصلات ضغط من مادة PVC، مما يوفر عزلًا مقاومًا للعوامل الجوية أو الماء. مع ذلك، لا يُعدّ PVC مناسبًا للاستخدام في الأماكن ذات درجات الحرارة العالية أو الصدمات العالية، ويجب حمايته من التعرض المباشر للأشعة فوق البنفسجية ما لم يكن مُصممًا للاستخدام الخارجي.
4. كيفية اختيار جسم القناة المناسب
اختيار هيكل الأنبوب المناسب لا يقتصر على الشكل فحسب، بل يعتمد أيضًا على نوع الأنبوب، وطريقة التوصيل، والبيئة، ومتطلبات الكود. اتخاذ القرار الصحيح يضمن سلاسة التركيب، وسهولة الصيانة، والامتثال الكامل للكود.
📍 قم بمطابقة مسار القناة
الخطوة الأولى هي فهم كيفية تحريك القناة الخاصة بك.
للحصول على دوران بزاوية 90 درجة نحو الحائط أو العلبة، استخدم جسم LB.
إذا كنت ستدور إلى اليسار أو اليمين حول الزاوية، فاختر LL أو LR.
بالنسبة للفرع ثلاثي الاتجاهات، استخدم جسمًا على شكل حرف T.
إذا كنت بحاجة إلى توصيل أربعة اتجاهات، ففكر في استخدام جسم على شكل X.
في المسارات المستقيمة الطويلة، يوفر الجسم C نقطة وصول متوسطة لسحب الأسلاك.
تم تصميم كل نوع للحفاظ على نصف قطر الانحناء المناسب مع السماح بالوصول إلى الموصلات في النقاط الرئيسية.
📐 حدد نوع الاتصال الصحيح
تتوفر أجسام الأنابيب بنسختين: ملولبة وغير ملولبة (ناعمة). يجب أن يتوافق النوع الذي تختاره مع مادة الأنابيب وطريقة التوصيل.
تُستخدم المحاور الملولبة مع الأنابيب المعدنية الصلبة (RMC)، أو الأنابيب المعدنية المتوسطة (IMC)، أو تجهيزات EMT. تُثبّت هذه الهياكل بمسامير على أطراف الأنابيب الملولبة أو المحولات الملولبة.
تُستخدم محاور ملساء مع أنابيب PVC، وتُربط باستخدام مادة لاصقة مُذيبة. صُممت هذه الهياكل للتوصيلات اللاصقة، ولا تحتوي على خيوط داخلية.
من الضروري استخدام نوع المحور الصحيح. قد تؤدي محاولة لصق الخيوط أو إدخال أنبوب ملولب بقوة في محور أملس إلى ضعف التوصيلات أو حدوث تسريبات أو مخالفات للوائح.
🧱اختر مادة مناسبة للبيئة
تُصنع أجسام الأنابيب من مواد تعمل بشكل مختلف في بيئات مختلفة:
يعتبر الألومنيوم والزنك المصبوب خفيف الوزن ومقاومًا للتآكل ومناسبًا للاستخدام الداخلي أو الخارجي الخفيف.
يوفر الحديد القابل للطرق أو الفولاذ المصبوب متانة عالية ويُستخدم غالبًا في المواقع الصناعية أو الخطرة.
يُعدّ PVC (غير المعدني) مثاليًا للبيئات الرطبة أو المدفونة أو المعرضة للتآكل. عند استخدامه مع أغطية وحشيات مانعة لتسرب الماء، يوفر أجسام أنابيب PVC عزلًا ممتازًا طويل الأمد.
بالنسبة للمناطق الخارجية أو تحت الأرض أو تحت الماء، غالبًا ما يتم تفضيل الخيارات غير المعدنية بسبب مقاومتها للصدأ والتلف الكيميائي.
📏 تأكيد حجم المحور وسعة الصندوق
يجب أن يكون حجم كل جسم موصل مناسبًا لنظام الموصل. تتراوح أحجام المحاور من نصف بوصة إلى 4 بوصات أو أكثر، ويجب أن تتناسب مع القطر الخارجي للموصل. كما يجب مراعاة الحجم الداخلي للموصل، خاصةً عند توصيل أو سحب موصلات متعددة.
استخدم تصنيف البوصة المكعبة الخاص بالشركة المصنعة للتأكد من وجود مساحة كافية لثني الأسلاك ونهاياتها.
إذا كان حشو السلك ضيقًا، فاختر إصدارًا عميقًا من الجسم لتمنح نفسك مساحة أكبر.
يساعد التحديد المناسب للحجم على تجنب ارتفاع درجة الحرارة، والضرر المادي، وعمليات التفتيش الفاشلة.
📘 تلبية متطلبات الكود
يُرجى دائمًا مراجعة قوانين الكهرباء المحلية قبل اختيار هيكل الأنابيب. تُحدد اللائحة الوطنية للكهرباء (المادة 314) متطلبات إمكانية الوصول، والحجم، والعزل البيئي. تشمل القواعد الرئيسية ما يلي:
يجب أن تتضمن الأنابيب الممتدة على أطوال معينة نقاط سحب يمكن الوصول إليها
يجب أن تكون الأغطية قابلة للإزالة دون إتلاف الجدران أو التشطيبات
في الأماكن الرطبة، يجب إدراج أجسام الأنابيب على أنها مقاومة للعوامل الجوية واستخدامها مع الحشيات
تقيد بعض المناطق استخدام مواد أو أشكال معينة (مثل أجسام X) في بيئات محددة، لذا من المهم التحقق من الامتثال في وقت مبكر من مرحلة التصميم.
5. الخاتمة
قد تبدو أجسام الأنابيب وكأنها مكونات صغيرة في نظام كهربائي، ولكن تأثيرها على تخطيط الأسلاك، وإمكانية الوصول إلى الصيانة، والامتثال للكود كبير.
من خلال فهم وظيفة كل نوع، يمكنك اتخاذ قرارات تخطيط أكثر ذكاءً وتجنب إعادة العمل المكلفة.
يضمن مطابقة حجم المحور ونوع الاتصال الصحيحين للقناة الخاصة بك تركيبات آمنة ومأمونة، في حين أن اختيار المادة المناسبة يحافظ على متانة النظام في ظل الضغوط البيئية.
سواء كنت تعمل على بناء سكني أو تجديد تجاري أو مشروع صناعي، فإن اختيار جسم الموصل المناسب يبسط عملك ويدعم نظامًا نظيفًا وقابلًا للصيانة.
مع التخطيط المناسب، فإن التركيبات الصحيحة لا تعمل على تحسين الكفاءة في الموقع فحسب، بل تضمن أيضًا صمود التثبيت الخاص بك أمام التفتيش والوقت.
في سي تيوب, نحن متخصصون في توفير هياكل أنابيب PVC عالية الجودة، مصممة لتلبية مجموعة واسعة من احتياجات التركيب. تتوفر هياكل أنابيبنا بأشكال قياسية متعددة - بما في ذلك LB، LL، LR، T، وC - وهي مصنوعة بمحاور لحام ملساء بالمذيبات وحشيات مدمجة لضمان توصيلات آمنة ومانعة لتسرب الماء، خاصةً في البيئات الخارجية أو الرطبة.
بالإضافة إلى عروضنا القياسية، ندعم أيضًا حلولاً مخصصة تلبي متطلبات مشروعك الفريدة، سواءً كان ذلك أحجام محاور غير قياسية، أو زوايا خاصة، أو وضع علامات. ينصب تركيزنا على مساعدة الكهربائيين والمقاولين ومصممي الأنظمة على بناء أنظمة توصيل أكثر أمانًا ونظافة وكفاءة.
نشكركم على قراءة هذه المقالة، ونأمل أن تكون قد ساعدتكم على فهم كيفية اختيار واستخدام أجسام الأنابيب بشكل أفضل. إذا كانت لديكم أي أسئلة أو احتياجات خاصة بمشروعكم، فلا تترددوا في التواصل مع فريقنا. نحن هنا لدعمكم بمنتجات عملية ونصائح احترافية.
الأسئلة الشائعة
س1: هل يمكن تركيب جسم القناة في الهواء الطلق؟
نعم، يمكن تركيب أجسام القنوات في الهواء الطلق، ولكن يجب التأكد من أنها مصممة للأماكن الرطبة.
للاستخدام الخارجي، يجب وضع علامة "مُبرّد" أو "مُقاوم للمطر" على جسم الأنبوب، واستخدامه مع غطاء مُحكم الإغلاق للحفاظ على إحكام الإغلاق. في البيئات المكشوفة، يُنصح باستخدام أنابيب غير معدنية (PVC) مع وصلات ملحومة بالمذيبات أو أجسام معدنية مقاومة للتآكل.
تأكد دائمًا من أن المنتج يحتوي على قوائم UL أو CSA المناسبة لتطبيقك.
س2: كيف أعرف هل أستخدم LB أم LL؟
يعتمد الاختيار بين LB وLL على الاتجاه الذي يحتاج مجرى الماء الخاص بك إلى الدوران فيه.
يدور جسم مجرى LB بزاوية 90 درجة من الأمام إلى الخلف - وهو ما يُستخدم غالبًا عندما يمتد المجرى على طول الحائط ويحتاج إلى الدخول إلى مبنى.
يدور جسم مجرى LL أيضًا بزاوية 90 درجة، لكن المخرج يدور إلى الجانب الأيسر عندما تواجه الغطاء.
من المفيد تصور مسار السلك: إذا كان من الضروري الذهاب مباشرة إلى اليسار، فاستخدم LL؛ إذا كان من الضروري الدخول مباشرة والانعطاف إلى الداخل (باتجاه الحائط)، فاختر LB.
س3: هل يمكن استخدام جسم الموصل كصندوق توصيل؟
في بعض الحالات، نعم. يمكن استخدام أجسام الأنابيب كنقطة وصل لتوصيل أو توصيل الموصلات، ولكن فقط إذا كان الحجم الداخلي كافيًا وكان القانون المحلي يسمح بذلك.
يسمح قانون الكهرباء الوطني (NEC) بالتوصيل في أجسام القنوات طالما أنها تلبي المساحة المطلوبة بالبوصة المكعبة للموصلات المعنية وتظل قابلة للوصول بعد التثبيت.
ومع ذلك، فهي ليست بديلاً لصناديق الوصلات كاملة الحجم في المواقف التي تحتوي على عدد كبير من الأسلاك أو اتصالات ذات تيار مرتفع.
س4: هل أحتاج إلى استخدام مادة مانعة للتسرب عند تركيب الغطاء؟
إذا تم تركيب جسم القناة في مكان رطب أو خارجي، فيجب عليك استخدام غطاء محكم الغلق، وفي بعض الحالات، تطبيق مركب مانع للتسرب غير متصلب حول مسامير الغطاء أو حوافه لتحسين مقاومة الماء.
تحتوي العديد من الأغطية المقاومة للطقس على حشية مثبتة في المصنع، ولكن إذا لم يكن الأمر كذلك، فيمكنك شراء الحشيات بشكل منفصل.
بالنسبة للأماكن الجافة الداخلية، عادةً ما تكون الأغطية القياسية المثبتة بالبراغي كافية بدون مانع تسرب إضافي، ما لم يتم تحديد ذلك في تعليمات المنتج.