1. المقدمة
ثني الأنابيب هي عملية تشكيل أنابيب الأنابيب لتوجيه الأسلاك الكهربائية بكفاءة عبر تصميم المبنى، واستيعاب الجدران والأسقف والزوايا والميزات الهيكلية الأخرى.
لا تعد الأنابيب المنحنية بشكل صحيح ضرورية للحفاظ على سلامة الأنظمة الكهربائية فحسب، بل تلعب أيضًا دورًا مهمًا في الحفاظ على المشاريع أنيقة بصريًا وسهلة الوصول إليها للصيانة أو الترقيات المستقبلية.
إن أهمية ثني الأنابيب بدقة لا تقتصر على الحماية فحسب، بل تؤثر أيضًا على كفاءة المشروع وجمالياته وسلامته.
من خلال إنشاء انحناءات ناعمة ودقيقة، يمكن للكهربائيين تقليل الضغط غير الضروري على الأسلاك، ومنع الأضرار الناجمة عن الحواف الحادة أو الزوايا غير المناسبة، وضمان امتثال مسارات الأسلاك لقواعد البناء.
تجعل الانحناءات المنفذة بشكل جيد من السهل سحب الأسلاك عبر القنوات وتقليل المخاطر المحتملة المرتبطة بالأسلاك المفكوكة أو المكشوفة.
ومع ذلك، من المهم ثني الأنابيب وفقًا للوائح ذات الصلة. تحدد NEC حدودًا لعدد زوايا الانحناء المسموح بها، وللمرجع، يوضح الرسم البياني التالي المتطلبات المحددة لأنواع الأنابيب المختلفة.
بشكل عام، ذكر قانون الكهرباء الوطني (NEC) أنه لا ينبغي أن يكون هناك أكثر من ما يعادل أربعة أرباع الانحناءات (360 درجة في المجموع) بين نقاط السحب، على سبيل المثال، أجسام الأنابيب والصناديق.
| نوع القناة | إن إي سي |
|---|---|
| الأنابيب المعدنية الوسيطة (IMC) | 342.26 |
| الأنابيب المعدنية الصلبة (RMC) | 344.26 |
| الأنابيب المعدنية المرنة (FMC) | 348.26 |
| أنابيب معدنية مرنة مقاومة للسوائل (LFMC) | 350.26 |
| أنابيب البولي فينيل كلوريد الصلبة (PVC) | 352.26 |
| البولي إيثيلين عالي الكثافة (HDPE) | 353.26 |
| الأنابيب غير المعدنية تحت الأرض مع الموصلات (NUCC) | 354.26 |
| أنابيب الراتنج المقوى بالحرارة (RTRC) | 355.26 |
| أنابيب مرنة غير معدنية مقاومة للسوائل (LFNC) | 356.26 |
| الأنابيب المعدنية الكهربائية (EMT) | 358.26 |
| الأنابيب الكهربائية غير المعدنية | 362.26 |
2. أنواع الأنابيب الكهربائية القابلة للانحناء وخصائصها
هناك أنواع عديدة من مواد الأنابيب، مثل EMT، وPVC، والمعادن الصلبة، ولكل منها سلوك مختلف عند الثني. يجب أن تكون الأدوات المستخدمة في الثني، سواءً يدوية أو كهربائية أو هيدروليكية، متوافقة مع نوع وحجم الأنابيب لتجنب التلف والحصول على نتائج دقيقة.
| نوع القناة | تفاصيل |
|---|---|
| الأنابيب المعدنية الكهربائية (EMT) | خفيف الوزن وسهل الثني، ويُستخدم عادةً في الأماكن المغلقة، وخاصةً في المباني التجارية والصناعية. يوفر هيكله المعدني الرقيق حمايةً كافيةً في البيئات الخاضعة للرقابة، ويمكن ثنيه يدويًا أو باستخدام أدوات ثني كهربائية. |
| أنابيب بلاستيكية صلبة | هذا النوع من الأنابيب مصنوع من كلوريد البوليفينيل، وهو مقاوم للتآكل ومثالي للبيئات الخارجية أو الرطبة. يمكن تسخين أنابيب PVC وتشكيلها لتناسب انحناءات محددة، مما يجعلها متعددة الاستخدامات للتركيبات الداخلية والخارجية، خاصةً حيث تكون مقاومة الرطوبة مهمة. |
| الأنابيب المعدنية الصلبة (RMC) | بفضل متانته العالية وجدرانه السميكة، يتميز RMC بالمتانة ومناسبته للبيئات عالية الضغط أو المكشوفة، مثل المنشآت الصناعية أو المنشآت الخارجية. يوفر RMC حماية قوية، ولكنه يتطلب أدوات ثني أكثر قوة، مثل النماذج الهيدروليكية أو الكهربائية، لتحقيق ثني دقيق. |
| الأنابيب المعدنية الوسيطة (IMC) | يُعدّ IMC أخف وزنًا بقليل من RMC، ولكنه يبقى متينًا ومناسبًا للاستخدام الخارجي أو التجاري. مع أنه يُمكن ثنيه أحيانًا باستخدام ثنيات يدوية عالية الرفع للأنابيب صغيرة القطر، إلا أنه يُنصح عادةً باستخدام ثنيات كهربائية أو هيدروليكية للحصول على نتائج أنظف، خاصةً للأنابيب ذات الأحجام الأكبر. |
| ملخص | إن فهم خصائص أنواع الأنابيب المختلفة واختيار تقنية الانحناء المناسبة لكل منها يضمن المتانة والسلامة في أي إعداد كهربائي. |
3. أنواع ثنيات الأنابيب ومتى يُستخدم كلٌّ منها
يُعد اختيار آلة ثني الأنابيب المناسبة أمرًا بالغ الأهمية لضمان الدقة والكفاءة والسلامة. يتطلب كل نوع من الأنابيب، نظرًا لخصائصه المادية الفريدة وسمكه، أسلوبًا خاصًا في الثني.
على سبيل المثال، تسمح مرونة أنابيب EMT بثنيها بسهولة باستخدام أدوات الثني اليدوية أو الكهربائية، بينما تتطلب صلابة أنابيب RMC قوة إضافية من أدوات الثني الهيدروليكية أو الكهربائية لتحقيق زوايا دقيقة دون إتلاف الأنابيب. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، تتطلب أنابيب PVC، التي تكون هشة عند تعرضها للبرودة، تسخينًا قبل الثني لمنع التشققات.
سنقوم بعمل مقدمة مفصلة لأنواع مختلفة من ثني الأنابيب وإجراء مقارنات فيما يلي.
| نوع من الثني | وصف | المزايا | العيوب |
|---|---|---|---|
| ثني اليدين | أدوات يدوية مصنوعة عادة من الحديد أو الألومنيوم، وتستخدم للأنابيب الأصغر حجمًا. | - محمول وسهل الاستخدام - فعالة من حيث التكلفة للمشاريع الصغيرة - مناسب لأنابيب EMT مقاس ½ و¾ و1 |
- يتطلب قوة يدوية كبيرة للأحجام الأكبر - يقتصر على أحجام الأنابيب الأصغر |
| الثنيات الميكانيكية | يتم تشغيلها يدويًا ولكنها تتطلب قوة أقل من ثني اليد؛ مناسبة للأحجام الأكبر. | - أكثر كفاءة من ثنيات اليد - أفضل للانحناءات المنتظمة - سريع وفعال |
- أثقل وأقل قابلية للحمل من أدوات الثني اليدوية |
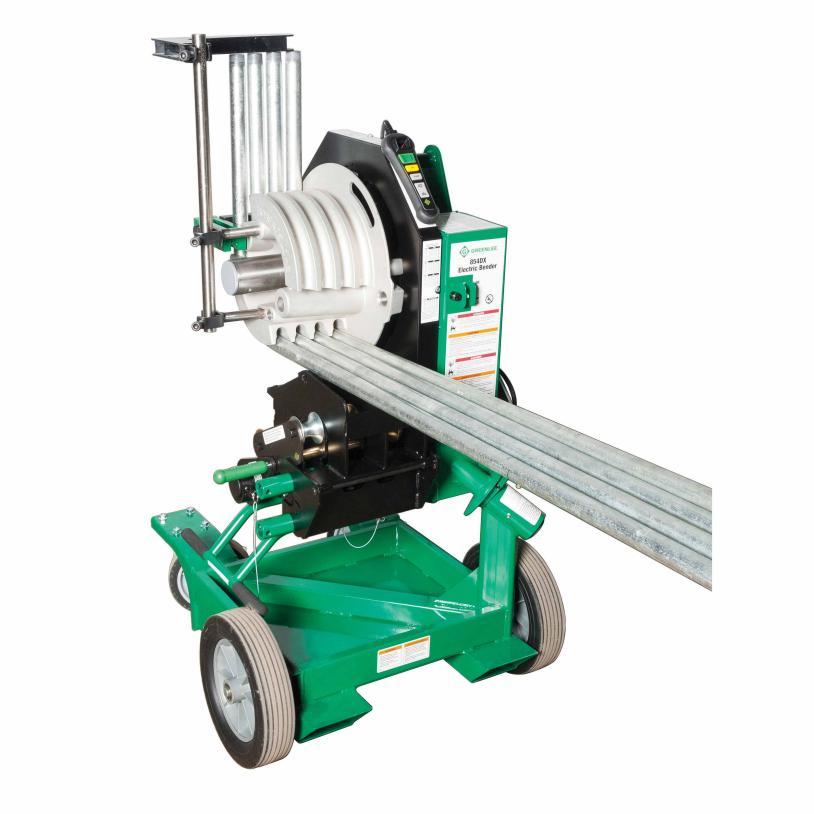
| ثنيات كهربائية | تعمل بالكهرباء، ومصممة للانحناء بكميات كبيرة. | - إعدادات قابلة للبرمجة للانحناءات المتكررة - مناسب لأنواع مختلفة من الأنابيب التي يصل حجمها إلى 2 بوصة - ينتج انحناءات سلسة ومتسقة دون إتلاف القناة |
- تكلفة أعلى - يتطلب مصدر طاقة كهربائية - ضخم ويتطلب مساحة للإعداد |
| ثنيات هيدروليكية | استخدم الضغط الهيدروليكي لثني الأنابيب الأكبر حجمًا (عادةً 2 بوصة أو أكثر). | - مثالية للمشاريع الكبيرة | - أكثر تكلفة بسبب المكونات الهيدروليكية |

تُعد نوابض الانحناء أداة مفيدة مصممة خصيصًا للمساعدة في ثني الأنابيب المرنة غير المعدنية مثل أنابيب PVC.
من خلال إدخال زنبرك انحناء داخل القناة أو حولها، فإنه يعمل على تعزيز جدران القناة أثناء عملية الانحناء، مما يمنعها من الانهيار أو الانحناء.
يُعد هذا مفيدًا بشكل خاص عند العمل مع أنابيب PVC ذات القطر الأصغر، والتي قد تكون عرضة للتشوه عند ثنيها يدويًا.
أفضل التطبيقات: تُستخدم نوابض الانحناء عادةً في الأنابيب المرنة خفيفة الوزن في التركيبات الكهربائية السكنية والتجارية الخفيفة. وهي مثالية للمشاريع التي تتطلب انحناءات سلسة وتدريجية، حيث لا تتطلب آلات ثقيلة أو أدوات عالية الدقة.
المميزات: نوابض الانحناء خفيفة الوزن، واقتصادية، وسهلة الاستخدام. توفر دعمًا إضافيًا لتحقيق انحناءات ثابتة دون إتلاف الأنابيب، مما يجعلها عملية للتعديلات السريعة أثناء العمل والتركيبات الصغيرة.
العيوب: على الرغم من فعالية نوابض الانحناء في المواد الأخف وزنًا، إلا أن لها حدودًا. فهي عادةً ما تكون مناسبة فقط للأنابيب الصغيرة غير المعدنية، لأنها قد لا توفر دعمًا كافيًا للمواد السميكة أو الصلبة مثل الأنابيب المعدنية.
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، تتطلب نوابض الانحناء بعض الجهد اليدوي، وهو ما قد لا يكون عمليًا للمشروعات الأكبر أو عندما تكون الزوايا الدقيقة ضرورية.
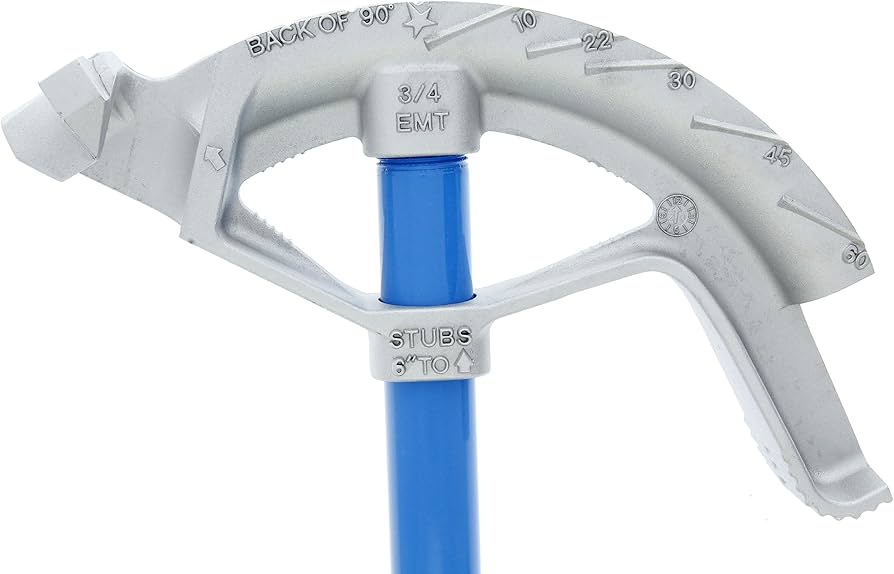
● ثني الأنابيب اليدوية
تعد أدوات ثني الأنابيب اليدوية أدوات تقليدية يتم تشغيلها يدويًا وتسمح للكهربائيين بثني الأنابيب باستخدام قوتهم الفيزيائية الخاصة.
وهي تتضمن عادةً رافعة وقالب نصف قطري للمساعدة في توجيه القناة عبر الانحناءات البسيطة، مثل الزوايا البالغة 90 درجة أو المنحنيات الطفيفة.
تعتبر أدوات ثني اليد خفيفة الوزن وقابلة للحمل ومثالية للمشاريع التي تتطلب القليل من الانحناءات.
أفضل التطبيقات: تعتبر أدوات ثني اليد مناسبة لثني الأنابيب الأصغر والأخف وزناً، مثل الأنابيب المعدنية الكهربائية (EMT) والأنابيب المعدنية المتوسطة ذات القطر الصغير (IMC).
تُستخدم هذه المواد بشكل متكرر في الأماكن السكنية والتجارية الخفيفة حيث قد يتطلب التصميم الكهربائي انحناءات أساسية فقط.
المميزات: هذه الأدوات سهلة الحمل، ولا تحتاج إلى كهرباء، مما يجعلها مثالية للمشاريع الصغيرة. كما أنها سهلة الاستخدام وفعالة في الحالات التي لا تتطلب دقة ثني معقدة.
العيوب: تتطلب هذه الآلات جهدًا بدنيًا لتشغيلها، مما قد يُرهقها عند التعامل مع أنواع الأنابيب الأكبر حجمًا أو الأكثر سمكًا. قد لا تكون آلات الثني اليدوية مناسبة لأنابيب المعادن الصلبة (RMC) أو الأنابيب ذات الجدران السميكة الأخرى التي تتطلب قوة أكبر للثني.
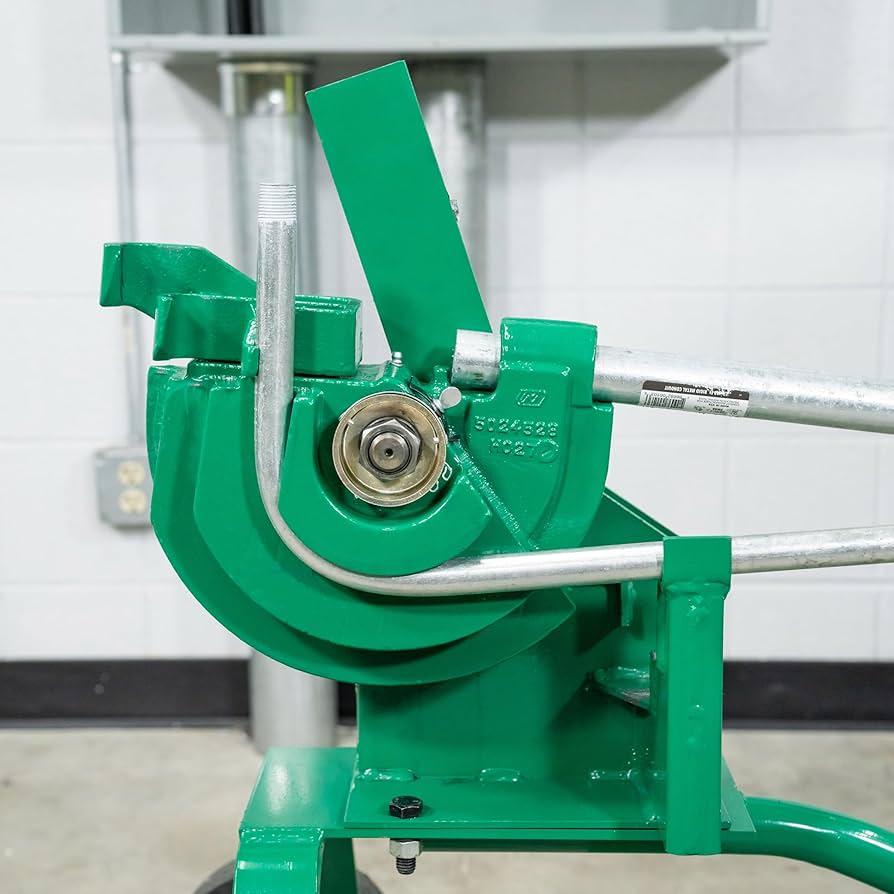
● ثنيات الأنابيب الميكانيكية
تستخدم ماكينات ثني الأنابيب الميكانيكية مساعدة ميكانيكية، مثل آلية الرفع أو ميزات الرفع الأخرى، لزيادة القوة المطبقة، مما يجعلها فعالة لثني الأنابيب السميكة أو ذات القطر الأكبر. غالبًا ما تتضمن أدلة مدمجة ومؤشرات زاوية للمساعدة في إجراء ثنيات دقيقة وهي مناسبة للتطبيقات الأكثر تطلبًا.
أفضل التطبيقات: تُستخدم أدوات الثني الميكانيكية عادةً لثني الأنابيب ذات الأحجام الكبيرة أو المواد شديدة التحمل، مثل الأنابيب المعدنية الصلبة (RMC) أو الأنابيب المعدنية المتوسطة (IMC). وهي مفيدة في البيئات التجارية والصناعية التي تتطلب تصميمات ثني أكثر تعقيدًا.
المميزات: تتطلب هذه الأدوات جهدًا بدنيًا أقل من أدوات الثني اليدوية، وتوفر تحكمًا ودقة أكبر. أما أدوات الثني الميكانيكية، فهي أنسب للحالات التي تتطلب التكرار والدقة، خاصةً في التركيبات الكهربائية المعقدة أو عالية المخاطر.
العيوب: عادةً ما تكون أدوات الثني الميكانيكية أغلى ثمناً وأضخم حجماً وتتطلب وقتاً أطول في الإعداد من أدوات الثني اليدوية. كما أنها قد لا تكون ملائمةً للثني السريع والبسيط في الأنابيب خفيفة الوزن.

4. كيفية اختيار أداة الثني المناسبة لمختلف أحجام الأنابيب والمواد
| حجم القناة | نوع القناة | بيندر الموصى به | ملحوظات |
|---|---|---|---|
| ½” إلى 1″ | فني طوارئ طبية، فني طب داخلي، فني طب رئوي | ثني اليد | محمول؛ جيد للمهام الخفيفة |
| من 1 بوصة إلى 2 بوصة | فني طوارئ طبية، فني طب داخلي، فني طب رئوي | ثني ميكانيكي أو كهربائي | رافعة مالية أفضل؛ خيارات قابلة للبرمجة متاحة |
| من 2½” إلى 5″ | شركة آر إم سي | آلة ثني هيدروليكية | ضروري للأحجام الأكبر والانحناءات المتسقة؛; |
| بولي فينيل كلوريد | بولي فينيل كلوريد | آلة ثني التسخين المتخصصة | ينعم المادة قبل الانحناء |
ضع في اعتبارك حجم ومادة القناة
● مواسير صغيرة (1/2 – 1 بوصة)
تعتبر الأنابيب ذات القطر الصغير، مثل تلك التي يتراوح قطرها بين 1/2 بوصة و1 بوصة، خفيفة الوزن وأسهل في التعامل بشكل عام.
بالنسبة لهذه الأنابيب، غالبًا ما يكفي استخدام آلة ثني يدوية، لأنها لا تتطلب قوة مفرطة لثنيها. تتميز آلات الثني اليدوية بسهولة حملها وسعرها المناسب وسهولة استخدامها، مما يجعلها مثالية لثني الأنابيب المعدنية الكهربائية (EMT) والأنابيب المعدنية المتوسطة (IMC) الأصغر حجمًا، والتي تُستخدم عادةً في المباني السكنية أو التجارية الخفيفة.
إن استخدام أداة الثني اليدوية لهذه الأحجام الأصغر يسمح للكهربائيين بالتحكم في الثني عن كثب وإنشاء زوايا ناعمة ودقيقة.
● مواسير متوسطة الحجم (1 – 2 بوصة)
الأنابيب التي يتراوح قطرها بين بوصة وبوصتين أثقل وزنًا وتتطلب قوة أكبر للثني مقارنةً بالأنابيب الأصغر. في حين أن آلة الثني اليدوية قادرة تقنيًا على التعامل مع بعض هذه الأحجام، إلا أن آلات ثني الأنابيب الكهربائية غالبًا ما تكون خيارًا أفضل.
توفر ماكينات الثني الكهربائية الطاقة الإضافية اللازمة للأنابيب متوسطة الحجم، مما يجعل عملية الثني أسهل وأسرع، خاصةً عند الحاجة إلى ثنيات متعددة. كما أنها توفر الدقة والسرعة، وهو أمر بالغ الأهمية في المشاريع الكبيرة، مثل المنشآت التجارية، حيث يكون الوقت والدقة بالغي الأهمية. تستطيع ماكينات الثني الكهربائية التعامل مع أنابيب EMT وIMC وأنابيب RMC (أنابيب معدنية صلبة) أصغر حجمًا ضمن هذا النطاق، مما يوفر حلاً عمليًا للتطبيقات متوسطة التحمل.
● مواسير كبيرة (2 بوصة فأكثر)
تعتبر الأنابيب ذات القطر الكبير، عادةً 2 بوصة أو أكثر، صلبة للغاية وتتطلب قوة كبيرة للانحناء دون إتلاف المادة.
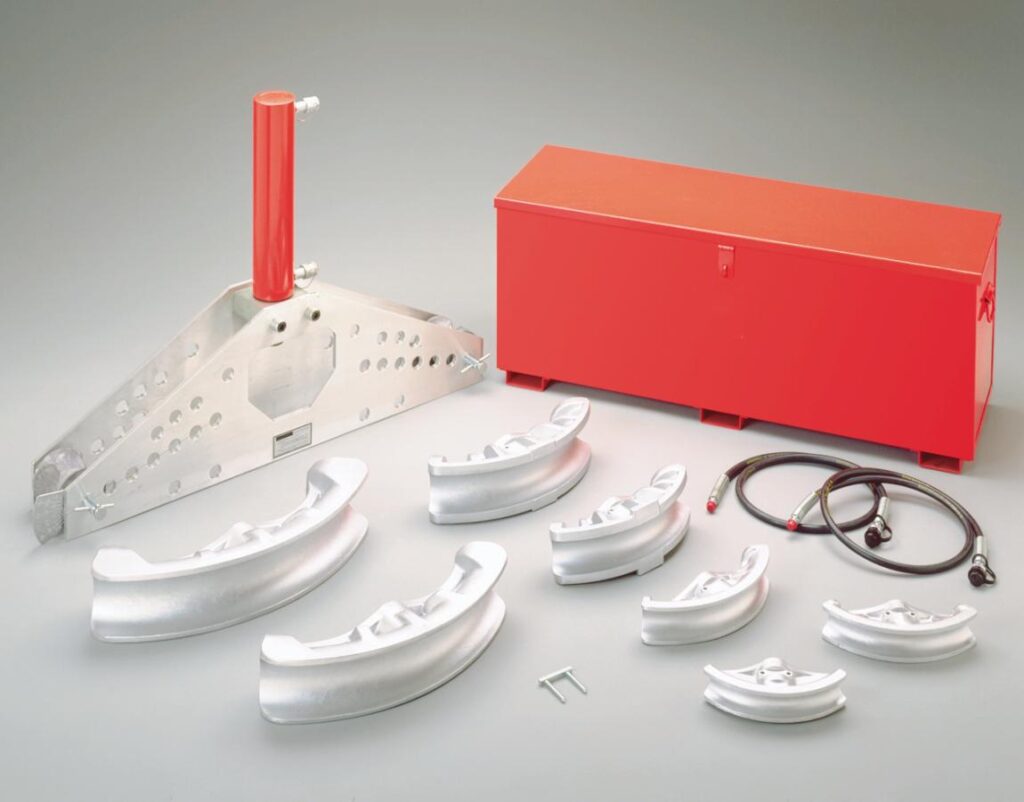
تُعدّ أدوات الثني الهيدروليكية الخيار الأمثل لهذه الأنابيب الكبيرة، إذ تستخدم سائلاً مضغوطاً لتطبيق قوة عالية ومتسقة، مما يضمن ثنياً سلساً ودقيقاً. تُستخدم أدوات الثني الهيدروليكية عادةً في المشاريع الصناعية والتجارية الثقيلة حيث يلزم ثني أنابيب الخرسانة المسلحة الكبيرة أو غيرها من الأنابيب ذات الجدران السميكة بزوايا محددة.
تتمتع هذه الثنايات بالقوة الكافية للتعامل مع المهام الأكثر تطلبًا، على الرغم من أنها تميل إلى أن تكون ثابتة ويتم تركيبها عادةً في ورش عمل أو مواقع ثابتة في مواقع العمل.
| عامل | ثني اليدين | الثنيات الميكانيكية | ثنيات كهربائية | ثنيات هيدروليكية |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| متطلبات القوة | يتطلب جهدًا يدويًا كبيرًا، خاصةً بالنسبة للأنابيب الأكبر حجمًا. | يقلل من الجهد مقارنة بأدوات ثني اليد؛ مناسب للأحجام المتوسطة. | يقلل من الجهد اليدوي؛ ويسهل استخدامه للأحجام الأكبر. | يزيل الجهد اليدوي بالكامل؛ ويستخدم المضخات الهيدروليكية للانحناء. |
| قابلية النقل | أكثر قابلية للحمل؛ مثالية للمهام الصغيرة أو المساحات الضيقة. | أقل قابلية للنقل من أدوات الثني اليدوية؛ ولا تزال قابلة للإدارة في مواقع العمل. | أقل قابلية للحمل؛ ضخم ويتطلب إعدادًا ومتطلبات طاقة؛ قد يحتاج إلى مساحة. | أقل قابلية للنقل بسبب الحجم ومصدر الطاقة. |
| التنوع | مناسب لأنواع مختلفة من الأنابيب (حتى 2 بوصة). | يقتصر على أحجام أصغر ولكن يمكن استخدامه على الأنابيب الصلبة إذا كان ذلك مناسبًا. | يتعامل مع مجموعة متنوعة من أنواع وأحجام الأنابيب مع ميزات قابلة للبرمجة. | تم تصميمها خصيصًا للأنابيب ذات القطر الأكبر؛ وهي أقل تنوعًا من الثنيات الكهربائية. |
| جودة الانحناء | قد يؤدي إلى انحناءات غير متناسقة إذا لم يتم استخدامه بشكل صحيح؛ ويتطلب مهارة. | مناسب للأحجام المتوسطة ومتعدد الاستخدامات لمختلف الانحناءات. | يقدم الدقة مع إعدادات قابلة للبرمجة؛ نتائج متسقة. | يوفر أعلى جودة للانحناءات دون تشوه؛ متسقة للغاية. |
| يكلف | الخيار الأكثر تكلفة؛ متاح لمحبي الأعمال اليدوية والمشاريع الصغيرة. | تكلفة معتدلة؛ أكثر تكلفة من ثنيات اليد ولكنها تقدم أداءً أفضل. | نقطة سعر أعلى بسبب الميزات والقدرات المتقدمة. | أعلى تكلفة بسبب المكونات والقدرات الهيدروليكية. |
اعتبارات خاصة بالمشروع
● حجم المشروع
يؤثر حجم المشروع بشكل كبير على نوع أداة ثني الأنابيب المطلوبة. بالنسبة للمشاريع السكنية الصغيرة، غالبًا ما تكون أدوات الثني اليدوية كافية نظرًا لأحجام الأنابيب الأصغر (عادةً من 1/2 بوصة إلى 1 بوصة) وأحمال العمل الأخف. تتطلب هذه المشاريع عادةً عددًا أقل من أدوات الثني، مما يجعل أداة الثني اليدوية عملية واقتصادية.
من ناحية أخرى، تتضمن المشاريع الصناعية أو التجارية الكبيرة أحجام قنوات أكبر وكميات أعلى من الانحناء، حيث تكون أدوات الانحناء الكهربائية أو الهيدروليكية أكثر ملاءمة.
غالبًا ما تتضمن المشاريع الصناعية مواد أكثر سمكًا وأنابيب ذات قطر أكبر، مما يتطلب القوة الإضافية والمتانة التي توفرها أدوات الثني الهيدروليكية أو الكهربائية.
بالنسبة لهذه التطبيقات واسعة النطاق، فإن اختيار الثني المناسب يمكن أن يوفر الوقت ويقلل من الضغط البدني ويضمن نتائج متسقة عبر الانحناءات المتكررة.
● الميزانية ومساحة العمل المتاحة
يمكن لميزانيات المشروع ومساحة العمل المتاحة أيضًا أن تساعد في اختيار الثني.
تعد أدوات الثني اليدوية الخيار الأكثر فعالية من حيث التكلفة ويمكن حملها، مما يجعلها مثالية للميزانيات الصغيرة أو المشاريع حيث تكون المساحة محدودة.
يمكن تخزين هذه الأدوات بسهولة واستخدامها في الأماكن الضيقة دون الحاجة إلى مصادر طاقة أو إعدادات خاصة.
ومع ذلك، إذا سمحت ميزانية المشروع، توفر أدوات الثني الكهربائية توازناً بين القدرة على تحمل التكاليف والقدرة المحسنة، مما يوفر السرعة والدقة للتطبيقات متوسطة الحجم.
بالنسبة للمشاريع الكبيرة ذات الميزانيات الكبيرة ومساحة العمل المخصصة، تُعدّ أدوات الثني الهيدروليكية استثمارًا مُجديًا نظرًا لقوتها العالية وكفاءتها العالية مع الأنابيب الكبيرة. تتطلب أدوات الثني الهيدروليكية عادةً مساحة إعداد أكبر وهي أقل قابلية للحمل، لذا فهي الأنسب لبيئات العمل الكبيرة حيث يُمكن استخدامها كمعدات ثابتة.
● مستوى الدقة المطلوب
يُعد مستوى الدقة المطلوب في المشروع عاملاً حاسماً أيضاً. إذا كانت الجوانب الجمالية أو الزوايا الضيقة مهمة، كما هو الحال في التركيبات المرئية أو المشاريع المعمارية، فإن آلات الثني الكهربائية والهيدروليكية قادرة على توفير ثنيات دقيقة ومتسقة، مما يقلل من احتمالية إعادة العمل.
توفر هذه الأدوات التحكم الدقيق وتقليل الأخطاء، مما يجعلها مثالية للمشاريع حيث تكون الدقة أمرًا بالغ الأهمية.
بالنسبة للمشاريع التي يكون فيها المظهر والدقة أقل أهمية - مثل قنوات المرافق المخفية في الجدران أو تحت الأرض - قد تكون الثنيات اليدوية كافية.
ومع ذلك، بالنسبة للتركيبات ذات الأنابيب المرئية، وخاصة في البيئات التجارية حيث تكون الجمالية والتوحيد أمرًا مهمًا، فإن الاستثمار في أداة ثني توفر الدقة والاتساق غالبًا ما يستحق التكلفة الإضافية.
4. تقنيات ثني الأنابيب بدقة

يُعدّ تحديد مسار الأنابيب بدقة أمرًا بالغ الأهمية. تُعدّ هذه العلامات بمثابة دليل لضمان حدوث الانحناءات في النقاط الدقيقة اللازمة لتصميم الأنابيب. ابدأ بتحديد نقطة بداية كل انحناء، مع القياس من نقطة ثابتة مثل نهاية الأنبوب.
شريط القياس أداة بسيطة لقياس أطوال الأنابيب بدقة. استخدمه لتحديد نقاط الانحناء والتحقق منها. هذه الخطوة بالغة الأهمية للانحناءات والزوايا التي تتطلب انحناءات متعددة.
الالتقاط هو مقدار طول الأنبوب الذي يمتصه الانحناء. أما الكسب فهو الطول الإضافي الناتج عن الانحناء، ويعود ذلك أساسًا إلى التمدد على طول الحافة الخارجية. غالبًا ما يوفر المصنعون مخططات الالتقاط للمساعدة في ضبط ذلك.
لثني بزاوية 90 درجة مع رفع 5 بوصات على موصل EMT 3/4 بوصة، للحصول على وصلة بطول 20 بوصة، ضع علامة عند 25 بوصة (20 + 5). هذا يُفسر فقدان طول الأنبوب الناتج عن الانحناء.
تحتوي معظم قواطع الأنابيب على مؤشرات درجات (10°، 30°، 45°، 90°). تساعد هذه المؤشرات على تكرار زوايا ثابتة عبر انحناءات متعددة.
توفر هذه الأدوات مستوى إضافيًا من الدقة. تُعدّ أدوات البحث الرقمية مفيدة بشكل خاص لتأكيد الانحناءات المخصصة أو ضمان دقة زوايا الانحناء.
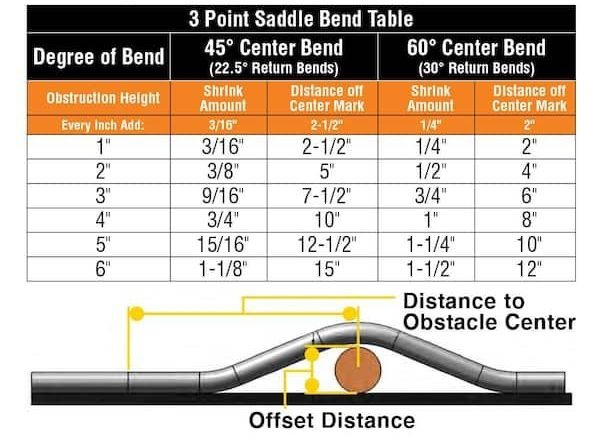
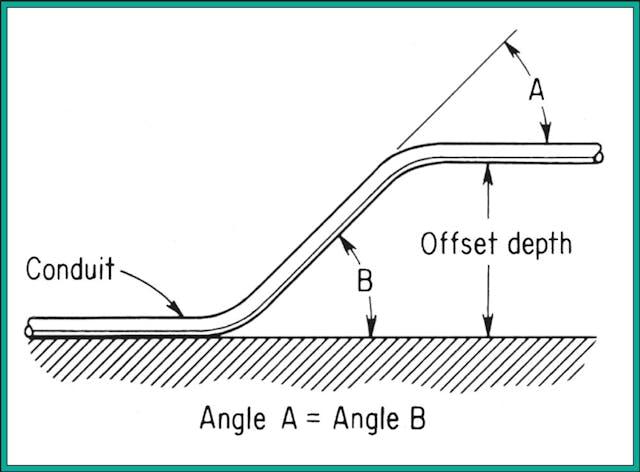
تستخدم الإزاحات انحناءين متطابقين. اضرب الارتفاع المطلوب في المضاعف (2.0 لزاوية 30 درجة، 2.6 لزاوية 22.5 درجة، 1.4 لزاوية 45 درجة) للحصول على التباعد. على سبيل المثال، ارتفاع 3 بوصات مع انحناءات 30 درجة يتطلب تباعدًا 6 بوصات.
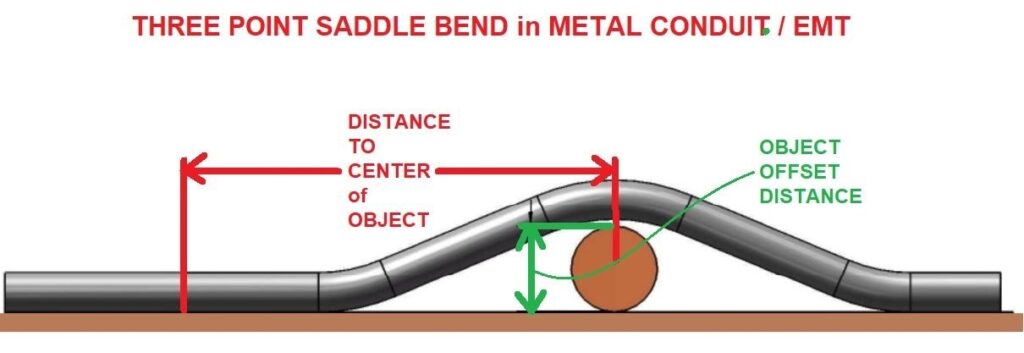
سرج ثلاثي النقاط: قِس ارتفاع العائق. انحنِ بزاوية ٤٥ درجة، وانحنِين خارجيين بزاوية ٢٢.٥ درجة.سرج ذو أربع نقاط: بالنسبة للعوائق الأكبر، استخدم أربع منحنيات — 22.5 درجة، 45 درجة، 45 درجة، 22.5 درجة — للحفاظ على مستوى القناة أثناء إزالة العائق.
5. أدوات وإكسسوارات لثني الأنابيب بدقة
إن وجود الأدوات والملحقات المناسبة يمكن أن يجعل عملية ثني الأنابيب أكثر كفاءة ودقة.
فيما يلي بعض الأدوات الأساسية التي يجب مراعاتها لضمان الدقة والاتساق في مشاريع ثني الأنابيب الخاصة بك:
حاسبة ثني الأنابيب
تُعد حاسبة انحناء القناة أداة قيمة لتحديد الأطوال والزوايا الصحيحة بسرعة لأنواع مختلفة من الانحناءات، مثل الإزاحات والسرج والانحناءات المتتالية.
يمكن استخدام الآلات الحاسبة يدويًا أو عبر تطبيق، وغالبًا ما تتضمن وظائف مُعدّة مسبقًا لحسابات الانحناء الشائعة، مما يجعلها مفيدة للغاية عند العمل على انحناءات متعددة على نفس الأنبوب. بإدخال القياسات الرئيسية، يمكنك الحصول على إرشادات فورية حول مكان وضع العلامات وثني الأنابيب، مما يقلل من خطر الأخطاء.
أداة تحديد الزاوية أو المنقلة
يساعد مُحدِّد الزوايا أو المنقلة على ضمان دقة الزوايا، خاصةً مع أدوات الثني اليدوية حيث قد تختلف الدقة. تُعدّ أدوات الثني الرقمية مفيدةً بشكل خاص في الحصول على انحناءات دقيقة، حيث تعرض قياس الزاوية آنيًا، مما يضمن دقة القياس.
بالنسبة لتخطيطات الانحناء المعقدة أو الزوايا المخصصة، يمكن أن يكون جهاز تحديد الزاوية ذا قيمة لا تقدر بثمن، مما يسمح لك بإعادة التحقق من الانحناءات قبل وأثناء التثبيت للتأكد من أنها تتوافق مع مواصفاتك.
المستوى أو المربع
يُعدّ استخدام ميزان تسوية (سواءً كان رقميًا أو سائلًا) أو مربعًا أمرًا بالغ الأهمية لضمان استقامة الأنابيب ومحاذاتها، خاصةً في المسارات الأفقية. يساعد استخدام ميزان التسوية على ضمان استواء الأنابيب وعدم ميلها دون قصد أثناء التركيب، وهو أمرٌ أساسيٌّ لكلٍّ من الأداء والمظهر.
تعتبر المربعات مفيدة بشكل خاص عند ثني أقسام متعددة تحتاج إلى الاتصال بسلاسة، حيث يمكنها التحقق من أن الانحناءات تحافظ على المحاذاة الصحيحة بالنسبة لأقسام القناة الأخرى.
قوالب للانحناءات المتعددة
عندما يتطلب المشروع عددًا كبيرًا من الانحناءات المتطابقة، كما هو الحال في التركيبات واسعة النطاق، فإن إنشاء قالب لتلك الانحناءات يمكن أن يوفر الوقت ويحافظ على التوحيد.
القوالب هي أدلة مصنوعة من أنبوب أولي منحني بشكل صحيح ويمكن وضعها جنبًا إلى جنب مع أقسام أخرى للتأكد من أنها تتطابق مع الزوايا والأطوال الأصلية.
يعد هذا مفيدًا بشكل خاص للمشاريع الكبيرة حيث يمكن أن تتراكم الانحرافات البسيطة وتؤثر على التصميم النهائي.
القوالب هي أدوات بسيطة ولكنها فعالة للغاية لتقليل الاختلافات عبر قنوات متعددة، مما يضمن مظهرًا متسقًا واحترافيًا ومحاذاة دقيقة في التخطيط العام.
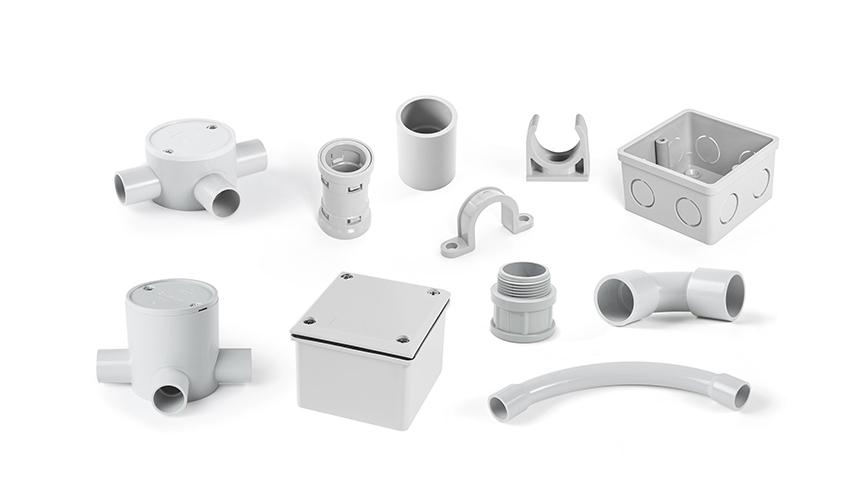
موصلات الأنابيب مساعدة في تحويل الزاوية
بالإضافة إلى ثني الأنبوب نفسه لتحقيق الدوران، فإن استخدام تجهيزات الأنابيب يمكن أن يوفر حلاً أكثر كفاءة وأقل ضررًا. تم تصميم هذه التجهيزات خصيصًا لإجراء دورات في نظام الأنابيب مع تقليل مخاطر إتلاف الأنبوب أو الأسلاك الموجودة بالداخل. من خلال استخدام التجهيزات، يمكن للمثبتين تحقيق دورات سلسة وخاضعة للرقابة دون إجهاد مادة الأنبوب، وهو أمر مفيد بشكل خاص لحماية الأسلاك الحساسة.
- موصلات الكوع: مُصممة لتوفير انعطافات سلسة بزاوية 90 درجة في أنظمة الأنابيب. متوفرة بزوايا مُتنوعة (عادةً 90 درجة و45 درجة)، وهي مثالية لتوجيه الأنابيب حول الزوايا والعوائق.
- انحناءات الكنس: بالنسبة لأحجام الأنابيب الأكبر، يوفر المسح منحنى أكثر تدريجيًا مقارنة بالكوع القياسي، مما يضمن انتقالًا أكثر سلاسة ويقلل الضغط على الأنابيب.
- موصلات ثلاثية ومتقاطعة: على الرغم من عدم استخدامها بشكل صارم للالتفاف حول الزوايا، فإن هذه الموصلات تمكن مسارات متعددة للقناة لتتبعها، والتي يمكن أن تشمل الالتفاف حول الزوايا.
- خيارات الأنابيب المرنة: يتم استخدامها في المنعطفات الضيقة أو المعقدة حيث لا تكون الموصلات الصلبة عملية - وخاصة في مناطق الآلات أو الأجزاء المتحركة.
6. الخاتمة
في هذا المنشور، استكشفنا الأنواع المختلفة من ماكينات ثني الأنابيب - اليدوية والكهربائية والهيدروليكية والتخصصية - كل منها مناسب لأحجام ومواد أنابيب معينة. كما قمنا بتغطية تقنيات الثني الأساسية، مثل القياس الدقيق وفهم المكسب والرفع واستخدام الأدوات المناسبة للثني المتسق والدقيق.
Ctube هي شركة مصنعة وموردة لأنابيب ووصلات PVC عالية الجودة، وتتخصص في توفير حلول مبتكرة ومتينة وفعالة من حيث التكلفة للتركيبات الكهربائية. تقدم Ctube مجموعة واسعة من خيارات الأنابيب، بما في ذلك جدول 40 القناة, جدول 80 القناة، والقنوات المتخصصة مثل دي بي 120 و النوع EB، مصممة للتطبيقات السكنية والصناعية على حد سواء.
في Ctube، ندرك أهمية الموثوقية والسلامة والأداء في أنظمة التوصيلات الكهربائية. يتم اختبار منتجاتنا بدقة للتأكد من أنها تلبي المعايير الصارمة، بما في ذلك مقاومة الضغط والصدمات ودرجات الحرارة القصوى، فضلاً عن الحماية من الأشعة فوق البنفسجية والتآكل. سواء كنت تعمل في تركيب تحت الأرض أو مشروع فوق الأرض، توفر Ctube التوصيلات والتجهيزات المناسبة لإنجاز المهمة بكفاءة وأمان.
الأسئلة الشائعة
1. ما هو الفرق بين ثني الأنابيب وموصل الأنابيب؟
ثني الأنابيب هو أداة تستخدم لثني الأنابيب نفسها لإنشاء زوايا ومنحنيات لتوجيه الأسلاك الكهربائية. من ناحية أخرى، يعد موصل الأنابيب تركيبًا يستخدم لربط قطعتين من الأنابيب أو تغيير اتجاه الأنابيب دون ثني المادة.
2. هل يمكنني ثني أنابيب PVC دون استخدام أداة ثني ساخنة؟
في حين أنه من الممكن ثني أنابيب PVC يدويًا دون حرارة باستخدام أداة ثني أنابيب PVC، فإن تطبيق الحرارة يمكن أن يساعد في تليين المادة، مما يسمح بثني أكثر سلاسة ودقة. بالنسبة للثنيات الضيقة أو المعقدة، من الأفضل استخدام أداة ثني PVC ساخنة لتجنب تشقق أو تجعد المادة.
3. كيفية ثني الأنابيب في الطقس البارد؟
قد يكون ثني الأنابيب في الطقس البارد أمرًا صعبًا، وخاصةً بالنسبة للأنابيب المصنوعة من مادة PVC وبعض الأنابيب المعدنية.
تدفئة الأنابيب: بالنسبة للأنابيب المصنوعة من مادة البولي فينيل كلوريد، استخدم مصدر حرارة مثل مسدس حراري لتدفئة الأنابيب قبل الانحناء. وهذا يجعل المادة أكثر مرونة ويقلل من خطر التشقق.
استخدم ضغطًا بطيئًا وثابتًا: تجنب تطبيق القوة بسرعة كبيرة، حيث يمكن أن يؤدي ذلك إلى ثني القناة بشكل غير متساوٍ أو كسرها في الظروف الباردة.
قم بتخزين المواد في مكان دافئ: إذا كان ذلك ممكنًا، احرص على إبقاء الأنابيب داخل المنزل أو في مكان دافئ حتى تصبح جاهزًا لاستخدامها. يساعد هذا في منع المواد من أن تصبح هشة للغاية.