1. المقدمة
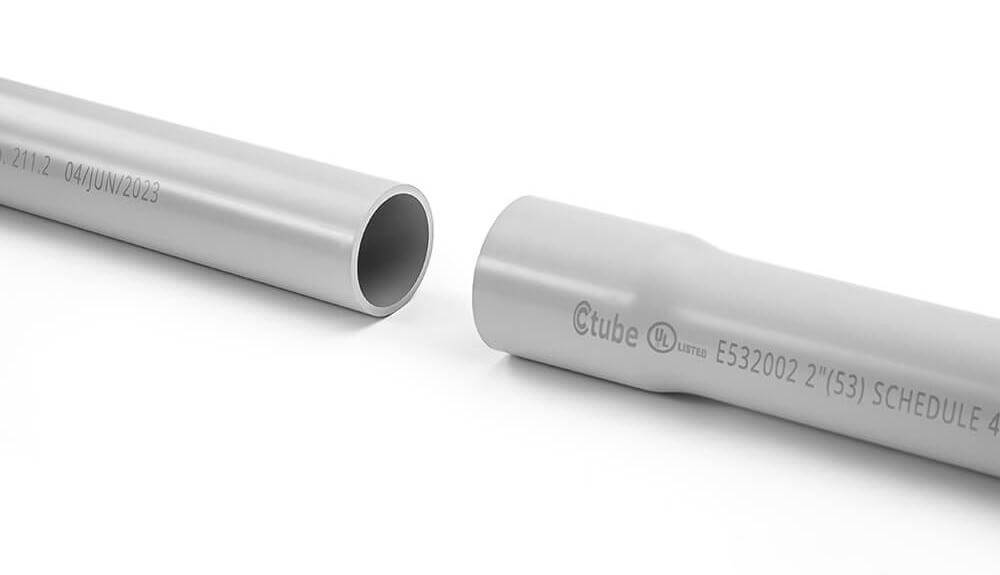
🔌 عندما يتعلق الأمر بحماية الأسلاك الكهربائية في المشاريع السكنية أو التجارية أو الصناعية، فإن أنابيب PVC من الجدول 40 هي واحدة من أكثر الحلول استخدامًا وموثوقية.
تُعرف أنابيب التوصيل من النوع Schedule 40 بمتانتها ومقاومتها للتآكل وفعاليتها من حيث التكلفة، وهي خيار مفضل لكل من التركيبات فوق الأرض وتحت الأرض.
🚧لكن ما المقصود تحديداً بـ "الجدول 40"؟ وكيف تتم مقارنته بأنواع أخرى من المواسير، مثل الجدول 80 أو المواسير المعدنية الصلبة؟
ما هي الشهادات التي يجب البحث عنها، مثل شهادة UL أو شهادة الامتثال لمعايير NEC؟ وما هو العمق المطلوب لدفنها لضمان استخدامها بشكل آمن وقانوني؟
💡 سواء كنت كهربائيًا مرخصًا أو مهندس مشروع أو مدير مشتريات، فإن هذا الدليل سيرشدك خلال كل ما تحتاج إلى معرفته حول أنابيب PVC من الجدول 40.
بدءًا من المواصفات التفصيلية واختبارات الأداء وصولاً إلى عمق التركيب والامتثال للمعايير، سنساعدك على اتخاذ خيارات مدروسة ونضمن أن نظامك الكهربائي مصمم ليدوم طويلاً.
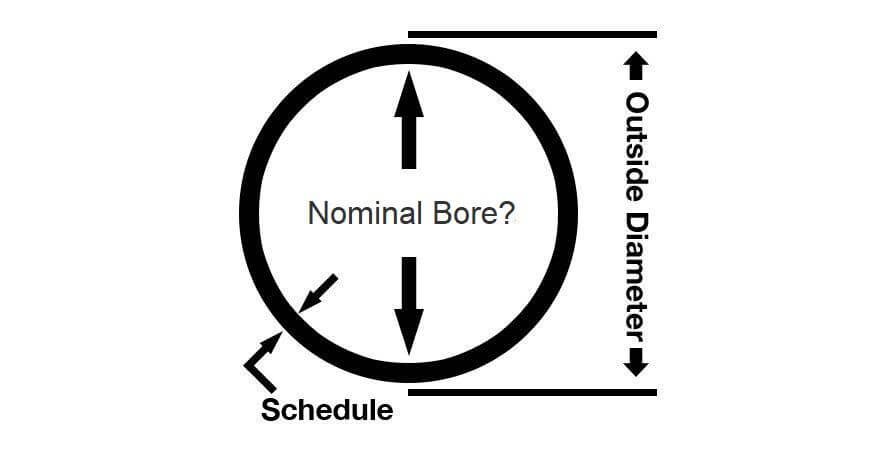
2. ماذا تعني كلمتا "Schedule" و "40" في سياق أنابيب PVC من الجدول 40؟
ربما رأيت مصطلح "الجدول 40" مطبوعًا على أنابيب PVC من قبل. ولكن ما معناه في الواقع؟
🤔 هل هو مقاس؟ أم تصنيف قوة؟ أم رمز ضغط؟ دعونا نحلل الأمر معًا.
🧱 ماذا تعني كلمة "جدول"؟
يشير مصطلح "الجدول" إلى معيار موحد يُستخدم لتحديد سُمك جدار الأنابيب أو المواسير. لا يقيس هذا المعيار الضغط بشكل مباشر، ولكن الجدران الأكثر سُمكًا غالبًا ما تعني أن المواسير قادرة على تحمل المزيد من الصدمات أو الإجهاد.
✅ فكر في "الجدول" كطريقة لتصنيف الأنابيب حسب سمك وقوة الجدران - ويعتمد ذلك على الحجم الاسمي للأنبوب (NPS).
📏 ما هو الحجم الاسمي للأنابيب (NPS)؟
يشير اختصار NPS إلى الحجم الاسمي للأنابيب، ويستخدم في أمريكا الشمالية لوصف القطر الخارجي للأنابيب.
يظل القطر الخارجي (OD) كما هو لكل حجم اسمي (مثل 2 بوصة، 3 بوصة، 4 بوصة).
يتغير سمك الجدار تبعًا للجدول (مثل 40 أو 80).
تُستخدم أنابيب الجدول 40 بشكل شائع في المنازل السكنية 🏠 والمباني التجارية 🏢 والتركيبات الأرضية الخفيفة 🚧.
إنه خيار متعدد الاستخدامات يلبي معايير الصناعة الرئيسية، بما في ذلك UL 651 للأنابيب الكهربائية و ASTM D1785 للأنابيب البلاستيكية المصنفة حسب الضغط.
وهذا يعني أن القطر الداخلي (ID) يتغير أيضًا.
🧮 على سبيل المثال:
يبلغ القطر الخارجي لأنبوب PVC من النوع Schedule 40 مقاس 2 بوصة 2.375 بوصة وسمك جداره 0.154 بوصة.
لذا فإن قطرها الداخلي يبلغ حوالي 2.067 بوصة.
إذن لا، ليس بالضرورة أن يحتوي الأنبوب الذي يبلغ قطره بوصتين على فتحة داخلية قطرها بوصتين 😄.
🔢 ماذا يخبرك "الجدول 40" في الواقع؟
“"الجدول 40" يعني أن الأنبوب له سمك جدار متوسط - سميك بما يكفي لمعظم التركيبات الكهربائية، ولكنه لا يزال خفيفًا وسهل التعامل معه.
تُستخدم أنابيب الجدول 40 بشكل شائع في المنازل السكنية 🏠 والمباني التجارية 🏢 والتركيبات الأرضية الخفيفة 🚧.
إنه خيار متعدد الاستخدامات يلبي معايير الصناعة الرئيسية، بما في ذلك UL 651 للأنابيب الكهربائية و ASTM D1785 للأنابيب البلاستيكية المصنفة حسب الضغط.
3. ما هي المواصفات الرئيسية لأنابيب PVC من النوع رقم 40؟
🧱 التركيب المادي: يتم تصنيع الأنابيب الكهربائية من الجدول 40 من مادة البولي فينيل كلوريد الصلبة (PVC)، وهي مادة لدائن حرارية.
📐 الأبعاد القياسية
| الحجم (بالبوصة) | القطر الخارجي (بوصة) | المعرف الحد الأدنى المتوسط (بوصة) | الحد الأدنى لسمك الجدار (بوصة) |
|---|---|---|---|
| نصف بوصة | 0.840 | 0.578 | 0.109 |
| 3/4 بوصة | 1.050 | 0.780 | 0.113 |
| 1 بوصة | 1.315 | 1.004 | 0.133 |
| 1-1/4 بوصة | 1.660 | 1.335 | 0.140 |
| 1-1/2 بوصة | 1.900 | 1.564 | 0.145 |
| 2 بوصة | 2.375 | 2.047 | 0.154 |
| 3 بوصات | 3.500 | 3.068 | 0.216 |
| 4 بوصة | 4.500 | 3.826 | 0.237 |
| 6 بوصات | 6.625 | 5.958 | 0.280 |
| 8 بوصة | 8.625 | 7.853 | 0.322 |
📌 ملحوظةهذا الجدول للاسترشاد فقط. قد تختلف الأبعاد الفعلية قليلاً بين الشركات المصنعة، وهذا أمر طبيعي تماماً، طالما أنها تقع ضمن الحدود المسموح بها وفقاً لمعايير UL وNEMA.
📏 الطول والوصلتتوفر هذه الأنابيب بأطوال مستقيمة تبلغ 3.05 متر (10 أقدام)، مع طرف متسع لتسهيل التوصيل باستخدام مادة لاصقة مذيبة. كما صُممت بعض الأنواع بوصلات مدمجة، مما يجعل التركيب أكثر سهولة.
4. ما هي متطلبات الاختبار التفصيلية لأنابيب PVC من الجدول 40؟
عند اختيارك لأنابيب PVC من النوع Schedule 40 لأعمال الكهرباء، فإن الأمر لا يتعلق فقط بالحجم أو سمك الجدار - فالسلامة والجودة لهما نفس القدر من الأهمية.
إذن كيف تعرف ما إذا كان استخدام قناة التوصيل آمناً؟ هنا يأتي دور شهادات مثل UL 651.
دعونا نستعرض معاني هذه المعايير - ولماذا يجب أن تهتم بها.
🔎 ما هو معيار UL 651؟
يرمز UL إلى مختبرات Underwriters Laboratories، وهي منظمة موثوقة تختبر المنتجات من حيث السلامة والأداء.
💡 اعتبر UL 651 بمثابة ختم موافقة - فهو يوضح أن القناة تم اختبارها وموثوق بها وجاهزة للاستخدام في الأنظمة الكهربائية الواقعية.
لضمان السلامة والأداء، يجب أن تستوفي أنابيب PVC من الجدول 40 متطلبات اختبار صارمة قبل أن تتمكن من حمل ملصق شهادة UL 651.
🧱 المواد والصنعة
قبل أي شيء آخر، دعونا نتحدث عما يتكون منه أنبوب PVC من النوع رقم 40 في الواقع.
لكي يتم إدراج المادة في قائمة UL، يجب أن تستوفي معيارًا عاليًا يُعرف باسم ASTM D1784، والذي يحدد قواعد نوع مركب PVC المسموح به.
وعلى وجه التحديد، يجب أن تفي أنابيب PVC الصلبة من الجدول 40 أو تتجاوز تصنيف الخلية 12123 - وهو رمز يحدد قوة المادة ومرونتها ومقاومتها للحرارة والصدمات.
✅ متطلبات معيار ASTM D1784-20 لمركبات PVC
وفق ASTM D1784-20, يجب أن يفي مركب PVC المستخدم في أنابيب الجدول 40 بمعايير أداء صارمة في المجالات التالية:
- قوة الشد - مدى قدرة المادة على التمدد قبل أن تنكسر
- مقاومة الصدمات - مدى تحمله للسقوط أو الضرب
- معامل المرونة – صلابة أو مرونة المادة
- درجة حرارة الانحراف – كيف يتصرف هذا المادة عند تعرضها للحرارة
- قابلية الاشتعال – كيفية تفاعل المادة مع النار أو مصادر الاشتعال
يتم توريد مادة PVC الخام عادةً على شكل مكعبات أو حبيبات أو مسحوق. يجب أن يكون:
- نظيف ومتناسق المظهر
- خالٍ من أي تلوث أو مواد غريبة
أثناء عملية التصنيع، قد تُضاف مواد آمنة إلى المركب لتحسين المعالجة والأداء. تشمل المواد المضافة الشائعة ما يلي:
- مواد التشحيم
- المثبتات
- أصباغ ملونة
- مواد مالئة – لتحسين خصائص البنية أو المعالجة
طالما أن مركب PVC النهائي يحتوي على الأقل 80% كلوريد الفينيل وبعد اجتياز جميع الاختبارات المطلوبة، تمت الموافقة على استخدامه في إنتاج المواسير الكهربائية من الجدول 40.
باختصار، هذا يعني أن كل قناة تبدأ بمواد عالية الجودة تم اختبارها بعناية - لذلك يمكنك الاعتماد على أداء موثوق به يدوم طويلاً.
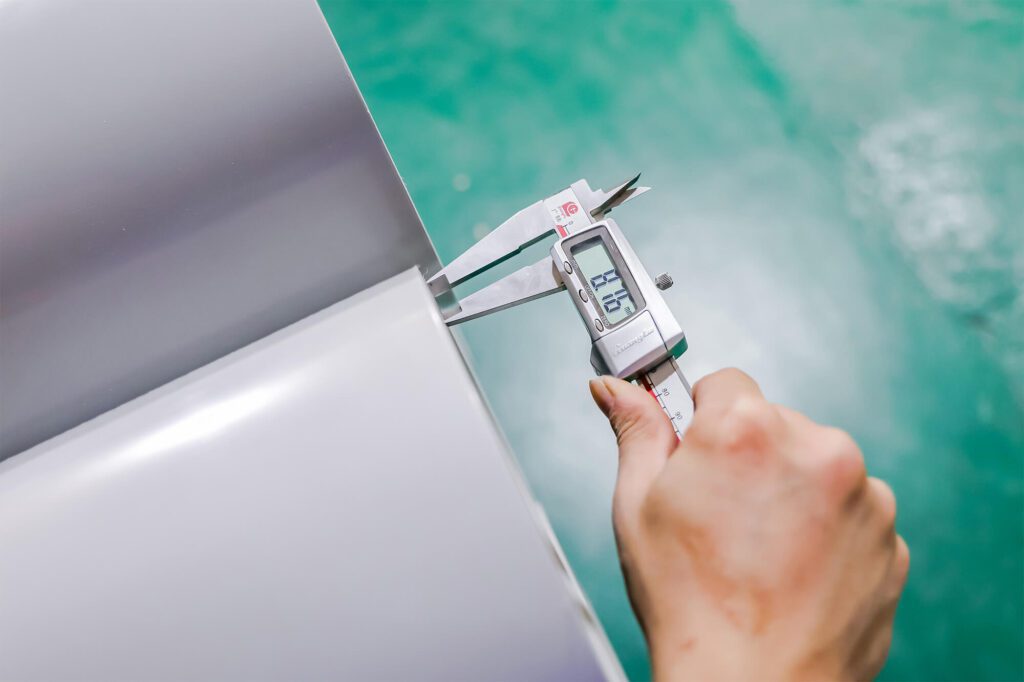
📏 أبعاد
عند اختيار المواسير، يُعدّ الحجم عاملاً بالغ الأهمية، ليس فقط لتمرير الأسلاك داخلها. فلكي تتوافق مواسير PVC من النوع Schedule 40 مع معايير UL 651 و ASTM، يجب أن تخضع لقواعد صارمة فيما يتعلق بقطرها الخارجي، وسُمك جدارها، وتفاوتات طولها. وهذا يضمن التناسق والسلامة والتوافق مع الوصلات وأنظمة المواسير الأخرى.
📌 ملحوظةكما ذكرنا سابقاً، قد تختلف القياسات الدقيقة - مثل القطر الخارجي، وسماكة الجدار، وتفاوت الطول - اختلافاً طفيفاً بين الشركات المصنعة. وهذا أمر طبيعي تماماً، طالما أن المنتج يلتزم بالتفاوتات المسموح بها والمحددة في معايير UL 651 أو ASTM.
🔬 شروط الاختبار
قبل بدء أي اختبار للأداء، يجب أن تخضع عينات أنابيب PVC من النوع رقم 40 لعملية تهيئة مسبقة. تضمن هذه الخطوة أن تكون نتائج الاختبار عادلة ودقيقة ومتسقة، بغض النظر عن الشركة المصنعة أو المختبر الذي يُجري الاختبار.
🕒 ما المقصود بالتكييف المسبق؟
يعني ذلك ببساطة وضع عينات الاختبار في بيئة مستقرة لفترة محددة قبل الاختبار. بالنسبة لأنابيب PVC من النوع رقم 40، إليك المتطلبات:
يجب تخزين جميع العينات لمدة 24 ساعة على الأقل في هواء ساكن، عند درجة حرارة
23.0 ±2.0 درجة مئوية (73.4 ±3.6 درجة فهرنهايت) قبل إجراء أي اختبارات أداء.
تساعد هذه الحالة القياسية على التخلص من تأثير عمليات التصنيع والنقل والتعرض البيئي الحديثة. فهي تسمح للمادة بالاستقرار في حالتها الطبيعية، بحيث تعكس الاختبارات كيفية أداء المنتج في التطبيقات العملية.
🌡️ لماذا هذه الدرجة من الحرارة؟
تُعرف درجة حرارة 23 درجة مئوية (أو 73.4 درجة فهرنهايت) بدرجة حرارة الغرفة في معايير الاختبار. وهي معيار عالمي يُستخدم في العديد من تقييمات المواد والمنتجات لضمان الاتساق.
✅ ما أنواع الاختبارات التي تستخدم هذا الشرط؟
تتطلب جميع اختبارات الأداء تقريبًا - مثل مقاومة الصدمات، وقوة السحق، وقوة الشد، وقابلية الاشتعال - تهيئة العينات مسبقًا بهذه الطريقة. وهذا جزء من بروتوكولات اختبار UL 651 و ASTM لضمان نتائج موثوقة.
🔬 كيف يتم اختبار أنابيب الجدول 40؟
| امتحان | متطلبات |
|---|---|
| قوة الشد | 5000 رطل لكل بوصة مربعة (34.5 ميجا نيوتن/م²) (3.45 كيلو نيوتن/سم²) (3515 جرام قوة/مم²) للجدول 40 |
| امتصاص الماء | يجب ألا يمتص الجدول 40 النهائي أكثر من 0.50% من وزنه الذاتي في الماء المقطر بعد 24 ساعة |
| مقاومة الصدمات | يجب ألا يتشقق أو يتمزق بطول يزيد عن 1/32 بوصة (0.8 مم) على طول السطح الخارجي |
| مقاومة اللهب | يجب ألا تتعرض العينات العمودية للهب لمدة تزيد عن 5 ثوانٍ بعد أي من عمليات تطبيق اللهب الثلاث التي تستغرق 60 ثانية (مع فترات فاصلة مدتها 30 ثانية). |
| مقاومة لأشعة الشمس | بعد 720 أو 1080 أو 1440 ساعة من التكييف، يجب الحفاظ على متوسط قوة تأثير إيزود* |
* تم إدراج جزء فقط من المحتويات للاطلاع عليها كمرجع فقط. يرجى الرجوع إلى معيار UL 651 للاطلاع على التفاصيل الكاملة.
* اختبار قوة الصدمة Izod هو طريقة قياسية معتمدة من ASTM لتحديد مقاومة الصدمات.
اختبار قابلية الاشتعال
يختبر معيار UL 94 تفاعل المادة مع اللهب ويصنفها بناءً على مدى سرعة انطفائها.
| فصل | توجيه عينة الاختبار | تعريف | الوقت المسموح به للحرق | يُسمح بإسقاط الكرة أثناء التدريب | ثقوب اللويحة |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UL 94 HB | أفقي | حرق بطيء | معدل احتراق أقل من 76 مم/دقيقة لعينة يقل سمكها عن 3 مم، ويتوقف الاحتراق قبل 100 مم | / | / |
| UL 94 V-2 | رَأسِيّ | توقف الحرق | الثلاثينيات | مشتعل: نعم غير قابل للاشتعال: نعم |
/ |
| UL 94 V-1 | رَأسِيّ | توقف الحرق | الثلاثينيات | الاشتعال: لا غير قابل للاشتعال: نعم |
/ |
| UL 94 V-0 | رَأسِيّ | توقف الحرق | 10 ثانية | الاشتعال: لا غير قابل للاشتعال: نعم |
/ |
| UL 94 5VB | رَأسِيّ | توقف الحرق | الستينيات | الاشتعال: لا غير قابل للاشتعال: لا |
نعم |
| UL 94 5VA | رَأسِيّ | توقف الحرق | الستينيات | الاشتعال: لا غير قابل للاشتعال: لا |
لا |
التصنيفات هي كما يلي:
قانون الكهرباء الكندي (CEC)، الذي نشرته جمعية المعايير الكندية، هو قانون السلامة الكندي للتركيبات الكهربائية الذي يتم اعتماده في القانون من قبل كل مقاطعة وإقليم مع تعديلات أو قواعد محلية.
يتضمن الكود إشارات إلى سلسلة اختبارات صارمة مصممة لاختبار مقاومة الأسلاك والكابلات للهب. تُصنّف الكابلات من FT1 إلى FT6، وذلك بحسب متطلبات اختبار اللهب المحددة التي تستوفيها.
وفيما يلي تفاصيل طرق الاختبار ومعايير التقييم:
| امتحان | يثبت | قوة اللهب | مدة | معايير النجاح/الرسوب |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FT1 | رَأسِيّ | 3000 وحدة حرارية بريطانية/ساعة | 5×15 ثانية | يجب ألا ينقل الموصل المُجهز اللهب أو يستمر في الاحتراق لأكثر من 60 ثانية بعد خمس مرات من تطبيق لهب الاختبار لمدة 15 ثانية لكل مرة. إذا احترق أكثر من 25% من الجزء الممتد من المؤشر، يُعتبر الموصل ناقلاً للهب. |
| FT2 | أفقي | 1700 وحدة حرارية بريطانية/ساعة | الثلاثينيات | يجب ألا يتجاوز طول الجزء المتفحم من عينة الحبل 100 ملم، كما يجب ألا تسقط منه جزيئات مشتعلة. |
| FT4 | رَأسِيّ | 70,000 وحدة حرارية بريطانية/ساعة | 20 دقيقة | يجب ألا تظهر الأسلاك أو الكابلات النهائية مواد متفحمة تتجاوز طول 1.5 متر (5 أقدام) من الحافة السفلية لوجه الموقد عند إخضاعها للاختبار. |
| FT5 | أفقي | 1700 وحدة حرارية بريطانية/ساعة | الستينيات | يجب ألا يتجاوز طول المنطقة المحترقة في الكابل 150 مم، ويجب ألا يستمر في الاحتراق لأكثر من أربع دقائق عند إخضاعه لاختبار اللهب. |
| FT6 | أفقي | 300,000 وحدة حرارية بريطانية/ساعة | 20 دقيقة | تُوصف مسافة انتقال اللهب التي لا تتجاوز 1.52 متر (5 أقدام)، وذروة الكثافة البصرية للدخان التي لا تتجاوز 0.5، ومتوسط الكثافة البصرية الذي لا يتجاوز 0.15 بأنها تتمتع بخصائص مقاومة للحريق وخصائص إنتاج دخان منخفضة. |
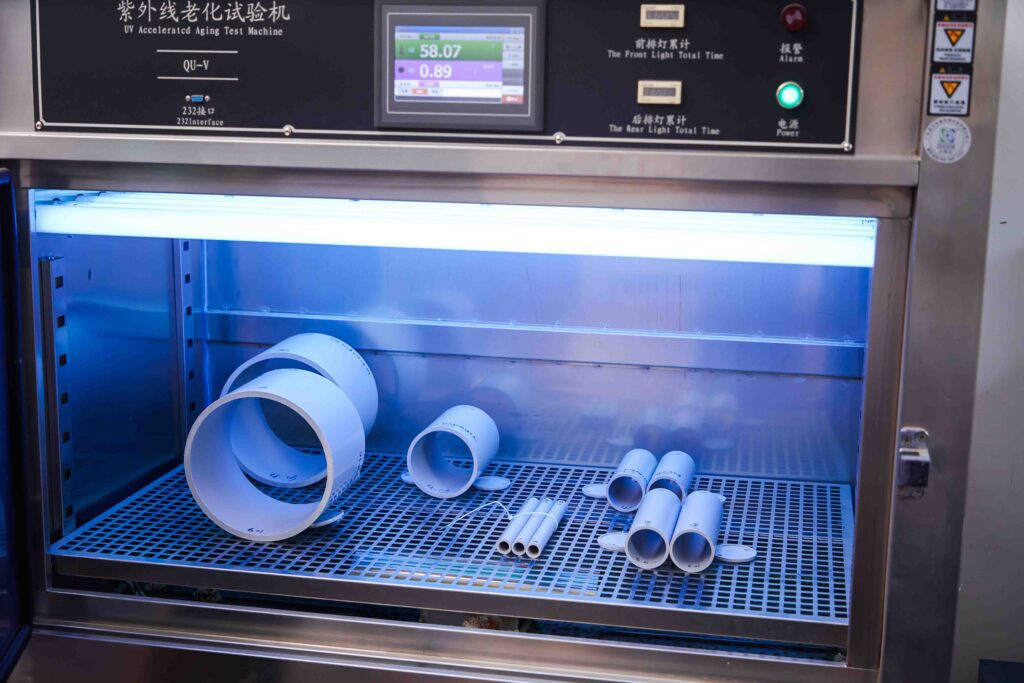
مقاومة الأشعة فوق البنفسجية
عندما تتعرض المواد البلاستيكية لأشعة الشمس لفترات طويلة، يمكن للأشعة فوق البنفسجية أن تكسر بنيتها الجزيئية.
🌞 تسمى هذه العملية بالتحلل الضوئي، وهي مشكلة كبيرة بالنسبة للمواد البلاستيكية الخارجية مثل قنوات الكهرباء.
إليكم ما يحدث:
تتسبب الأشعة فوق البنفسجية في تلف الروابط الكيميائية في البلاستيك.
وهذا يؤدي إلى تكوين الجذور الحرة - وهي ذرات صغيرة غير مستقرة تهاجم الجزيئات القريبة.
⚠️مع انتشار الضرر، يبدأ البلاستيك في التشقق وتغير اللون وفقدان القوة والمرونة.
وماذا يحدث عندما يحدث ذلك؟ إنه يعرض كابلاتك الكهربائية لخطر جسيم، خاصة في التركيبات الخارجية أو المكشوفة.
لضمان قدرة الأنابيب البلاستيكية على تحمل سنوات من التعرض لأشعة الشمس دون أن تتعطل، يقوم المصنعون بإجراء اختبارات خاصة للأشعة فوق البنفسجية.
🌤️ يحاكي هذا الاختبار التعرض لأشعة الشمس على المدى الطويل (مثل 8 سنوات!) في فترة زمنية قصيرة - حوالي 480 ساعة في المختبر.
يتحقق الاختبار من أمور مثل:
🔹 بهتان اللون
🔹 فقدان قوة الصدمة
🔹 انخفاض المرونة أو الهشاشة
🌎✅ يمكن أن يختلف ما يتم اختباره حسب التطبيق، لكن الهدف دائمًا هو نفسه: التأكد من أن المادة يمكنها الصمود تحت أشعة الشمس، تمامًا كما تفعل في الحياة الواقعية.
وضع العلامات
🛠️✅ يجب أن تحمل كل قطعة من أنابيب PVC من النوع رقم 40 علامات واضحة ودائمة. هذه العلامات ليست للزينة فقط، بل تُقدم معلومات مهمة وتساعد على ضمان مطابقة كل شيء للمعايير.
إليكم ما تتضمنه عملية وضع العلامات:
✅ رمز UL - هذا يعني أن القناة قد تم اختبارها واعتمادها بموجب معيار UL 651، وهو معيار أمان موثوق به.
🔤 نوع القناة (على سبيل المثال، "Schedule 40 PVC").
📘 رقم معيار UL.
🏭 اسم الشركة المصنعة.
📏 حجم الأنبوب (مثل 1/2 بوصة، 1 بوصة، إلخ).
تساعد هذه العلامات الفنيين والمفتشين على التحقق بسرعة من أن الأنابيب معتمدة ومناسبة للعمل. لا حاجة للتخمين!
5. ما هي التطبيقات الشائعة لأنابيب PVC من النوع رقم 40؟
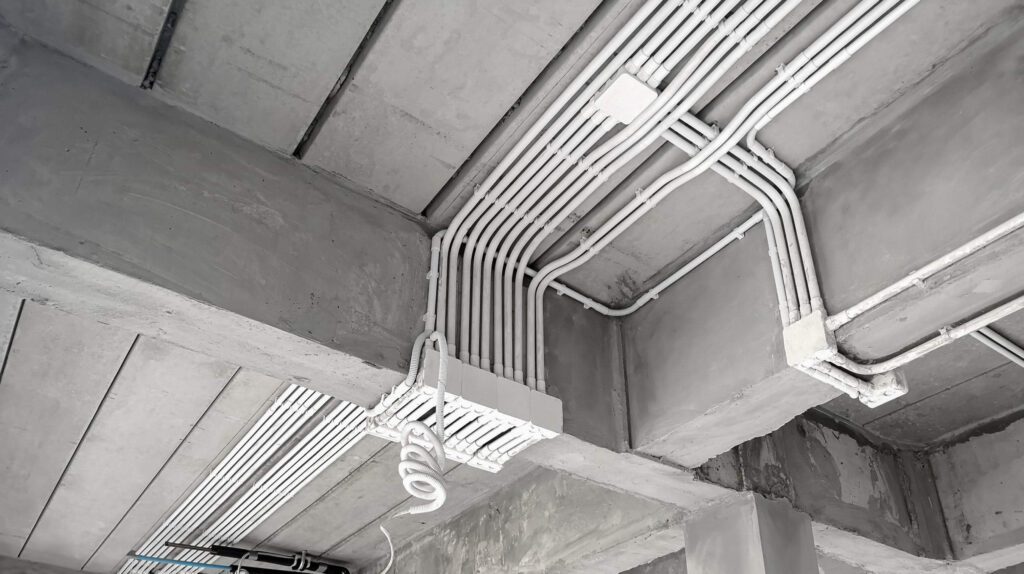
يُعدّ أنبوب PVC من النوع رقم 40 خيارًا متعدد الاستخدامات ومتينًا لتمديد الأسلاك الكهربائية. وبفضل مقاومته للرطوبة ومتانته، يمكن تركيبه فوق سطح الأرض أو تحتها، ويعمل بكفاءة في بيئات متنوعة.
🏡في المنازل السكنية
يُستخدم أنبوب PVC من النوع رقم 40 بشكل شائع لتمديد الأسلاك الكهربائية داخل المنازل - داخل الجدران، والأقبية، والعليات، والجراجات. كما أنه مثالي للاستخدامات الخارجية مثل إضاءة الحدائق، وخطوط الكهرباء الخارجية، وتمديدات المسابح، حيث يجب أن يكون الأنبوب مقاومًا للرطوبة والظروف الجوية. يُفضّله أصحاب المنازل لخفة وزنه، وسهولة قصه، ومتانته.
🏬 في المباني التجارية
في أماكن مثل المكاتب والمتاجر والمباني العامة، يساعد هذا الأنبوب في توجيه كابلات الطاقة والاتصالات. ستجده مخفيًا خلف الجدران والأسقف وتحت الأرضيات. إنه خيار اقتصادي وسهل التركيب، مما يجعله مثاليًا للمباني الجديدة ومشاريع التجديد على حد سواء.
🏗️في المنشآت الصناعية
تعتمد المصانع والمستودعات أيضاً على أنابيب PVC من النوع رقم 40. فهي تساعد على حماية الأسلاك من المواد الكيميائية والرطوبة والصدمات الفيزيائية، وكلها عوامل شائعة في البيئات الصناعية. وسواءً كانت معدات ثقيلة أو أنظمة آلية، فإن هذه الأنابيب تحافظ على سلامة الكابلات وسلاسة عملها.
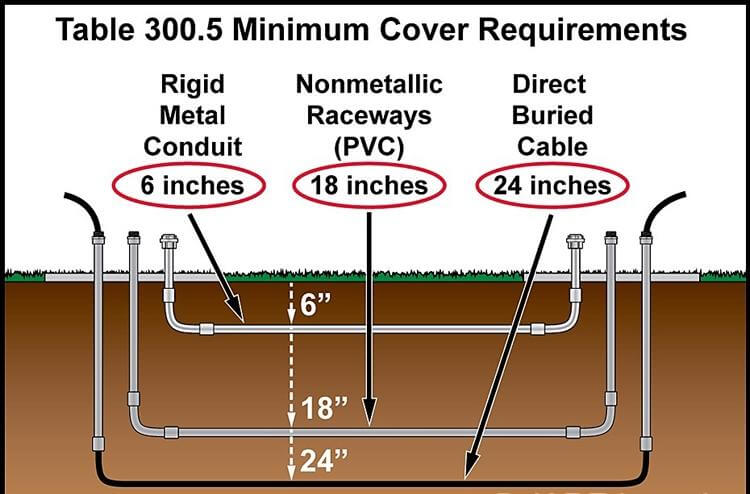
6. ما هو العمق الذي يجب أن تُدفن فيه أنابيب PVC من النوع رقم 40 تحت الأرض؟
🌱🛠️ إذا كنت تخطط لتمديد أنابيب PVC من النوع رقم 40 تحت الأرض، فستحتاج إلى اتباع إرشادات عمق الدفن لضمان سلامة التركيبات ومطابقتها للمعايير. تستند هذه الأعماق إلى توصيات قانون الكهرباء الوطني (NEC) وتساعد على منع التلف العرضي الناتج عن الحفر أو الأحمال الثقيلة.
| نوع التثبيت | الحد الأدنى لعمق الدفن | توضيح |
|---|---|---|
| الدفن المباشر | 18 بوصة (45 سم) | يجب أن يكون عمق الأنابيب الموضوعة مباشرة في التربة 18 بوصة على الأقل للحماية من الأدوات والحفر والأحمال السطحية. |
| غلاف خرساني | 6 بوصات (15 سم) | عندما يتم تغليف الأنابيب بالخرسانة، يتم تقليل العمق المطلوب بسبب الحماية الإضافية. |
| تحت لوح خرساني بسمك بوصتين | 12 بوصة (30 سم) | إذا تم تركيبه تحت بلاطة خرسانية بسمك 2 بوصة على الأقل، فإن عمق 12 بوصة مقبول لأن البلاطة توفر حماية معتدلة. |
| 💡 نصيحة احترافية: تحقق دائمًا من القوانين المحلية أو لوائح المرافق العامة - فقد يكون لدى بعض المناطق قواعد أكثر صرامة من قانون الكهرباء الوطني! | ||
ما الذي يؤثر على عمق دفن الأنابيب؟
🌍🚧 على الرغم من أن قانون الكهرباء الوطني (NEC) يُحدد قواعد عامة لعمق دفن أنابيب PVC من النوع 40، إلا أنه قد يلزم تعديل العمق الفعلي بناءً على ظروف الموقع. إليك بعض العوامل الرئيسية التي يجب مراعاتها قبل البدء بالحفر:
| عامل | توضيح |
|---|---|
| نوع التربة | - قد تتحرك التربة الرخوة أو الرملية، لذا فإن الدفن على عمق أكبر يساعد في الحفاظ على الاستقرار. - توفر التربة الكثيفة أو المتماسكة دعماً طبيعياً أفضل، مما يتطلب عمقاً أقل. |
| درجات الحرارة المتجمدة (خط الصقيع) | – في المناطق الباردة، يجب دفن الأنابيب تحت خط الصقيع. – يمكن أن تؤدي دورات التجمد والذوبان إلى تحريك التربة، مما يعرض الأنابيب لخطر التلف. – تحقق من قوانين البناء المحلية أو بيانات الصقيع الإقليمية. |
| أحمال المرور | - في حالة تركيبها تحت الممرات أو الطرق أو مواقف السيارات، قد تحتاج الأنابيب إلى دفن أعمق أو تغليف خرساني. – هذا يمنع الضرر الناتج عن الضغط والاهتزاز. |
| طريقة التركيب | – يتطلب الدفن المباشر عمقًا أكبر بسبب التعرض للعوامل الجوية. - يسمح الغلاف الخرساني بالدفن على عمق أقل من خلال توفير الحماية. |
✅ نصيحة: استشر دائمًا قانون الكهرباء المحلي أو فني كهرباء مرخصًا للتأكد من المتطلبات الدقيقة لمنطقتك. قد تختلف هذه المتطلبات عن معايير NEC بناءً على الظروف الإقليمية.
| المادة 300 - المتطلبات العامة لطرق ومواد التوصيل الكهربائي | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| الجدول 300.5 متطلبات الحد الأدنى للتغطية، من 0 إلى 1000 فولت، اسمي، الدفن بالملليمترات (البوصات) (نوع طريقة التوصيل أو الدائرة الكهربائية) |
|||||
| موقع طريقة التوصيل أو الدائرة | العمود 1 كابلات أو موصلات الدفن المباشر |
العمود 2 قناة معدنية صلبة أو قناة معدنية متوسطة |
العمود 3 قنوات غير معدنية مدرجة للدفن المباشر |
العمود 4 دوائر فرعية سكنية مصنفة بجهد 120 فولت أو أقل مزودة بقاطع تيار تسرب أرضي (GFCI) |
العمود 5 دوائر التحكم في الري وإضاءة المناظر الطبيعية |
| مم / بوصة. | مم / بوصة. | مم / بوصة. | مم / بوصة. | مم / بوصة. | |
| جميع المواقع غير المحددة أدناه | 600 / 24 | 150 / 6 | 450 / 18 | 300 / 12 | 150أ، ب / 6أ، ب |
| في الخندق الذي يقل سمكه عن 50 مم (2 بوصة) من الخرسانة أو ما يعادلها | 450 / 18 | 150 / 6 | 300 / 12 | 150 / 6 | 150 / 6 |
| تحت مبنى | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 (في مجرى السباق أو النوع MC أو MI) | 0 (في مجرى السباق أو النوع MC أو MI) |
| تحت بلاطة خرسانية لا يقل سمكها عن 102 مم (4 بوصات) في حالة عدم وجود حركة مرور، و152 مم (6 بوصات) بعد التركيب | 450 / 18 | 100 / 4 | 100 / 4 | 150 / 6 (دفن مباشر) 100 / 4 (في مسار السباق) |
150 / 6 (دفن مباشر) 100 / 4 (في مسار السباق) |
| تحت الشوارع والطرق السريعة والفرعية والأزقة والممرات ومواقف السيارات | 600 / 24 | 600 / 24 | 600 / 24 | 600 / 24 | 600 / 24 |
| ممرات سيارات ومواقف سيارات خارجية (للمنازل المكونة من عائلة واحدة أو عائلتين) | 450 / 18 | 450 / 18 | 450 / 18 | 300 / 12 | 450 / 18 |
| داخل أو تحت مدارج المطارات، بما في ذلك المناطق المجاورة المحظورة التعدي عليها | 450 / 18 | 450 / 18 | 450 / 18 | 450 / 18 | 450 / 18 |
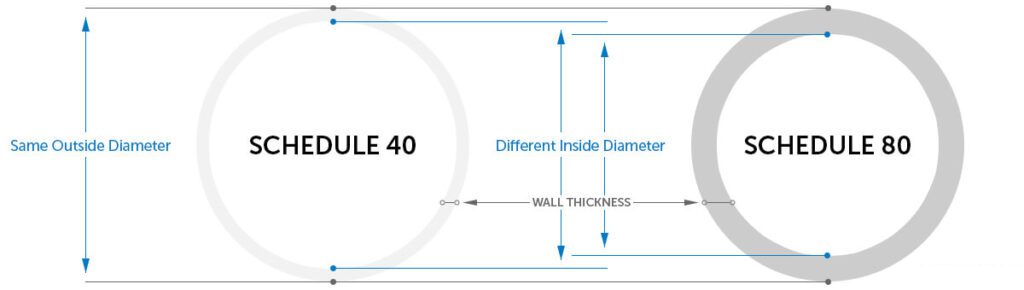
7. ما الفرق بين أنابيب PVC من النوع 40 والنوع 80؟
🔍يتم استخدام كل من أنابيب PVC من الجدول 40 والجدول 80 لحماية الأسلاك الكهربائية - لكنها مبنية بشكل مختلف قليلاً، وكل منها أنسب لأنواع معينة من الوظائف.
دعونا نلقي نظرة فاحصة على كيفية مقارنتهما:
| فئة | الجدول الزمني 40 | الجدول 80 |
|---|---|---|
| سمك الجدار | يتميز بجدار أرق، مما يجعله أخف وزنًا وأسهل في التعامل. وهو مثالي لمعظم الاستخدامات السكنية والتجارية الخفيفة التي لا تتطلب متانة فائقة. | يتميز بجدار أكثر سمكًا، مما يمنحه قوة أكبر ومقاومة للصدمات. هذه المتانة الإضافية تساعد على حماية الأسلاك في البيئات القاسية. |
| مقاومة الضغط والصدمات | يعمل بشكل جيد في المناطق التي لا تتعرض فيها الأنابيب لضغط شديد أو تلف مادي. مثالي للاستخدام العام في المنازل والمباني. | يتميز بتصنيف ضغط أعلى وهو مصمم لتحمل الظروف القاسية، كما هو الحال في المواقع الصناعية أو المناطق المعرضة لخطر الاصطدام. |
| يكلف | يُعدّ خيارًا اقتصاديًا أكثر لأنه يستهلك كمية أقل من المواد. وهو خيار ذكي لمعظم الأعمال العادية التي لا تتطلب قوة فائقة. | عادة ما تكون أغلى ثمناً نظراً لبنيتها السميكة ومتانتها المحسنة. |
| صعوبة التركيب | يتميز بسهولة وسرعة التركيب بفضل وزنه الخفيف ومرونته. كما أنه أسهل في القص والثني. | يصعب التعامل معها بسبب سمك جدارها. وقد يتطلب تركيبها جهداً وأدوات أكثر. |
8. الخاتمة
جدول 40 أنابيب PVC لا يزال خيارًا موثوقًا به في التركيبات الكهربائية السكنية والتجارية، وحتى في بعض الصناعات الخفيفة. إن توازنه بين المتانة وسهولة الاستخدام والفعالية من حيث التكلفة يجعله الحل الأمثل لحماية الأسلاك الكهربائية فوق الأرض أو تحتها أو المدفونة في الخرسانة.
من خلال فهم المعايير ذات الصلة ومتطلبات التركيب والاختلافات بين الجدول 40 وأنواع المواسير الأخرى مثل الجدول 80 أو RMC، يمكن للكهربائيين والمقاولين ضمان أنظمة كهربائية آمنة ومتوافقة وطويلة الأمد.
سواء كنت تخطط لمشروع صغير أو تدير مشروع بنية تحتية كبير، فإن اختيار منتجات عالية الجودة ومعتمدة - مثل تلك التي تقدمها Ctube - يمكن أن يحدث فرقًا كبيرًا في الأداء والسلامة.
سي تيوب’تتميز أنابيب PVC الصلبة من النوعين Schedule 40 و Schedule 80 بحصولها على شهادات UL و CSA، مما يوفر أداءً موثوقًا به في التطبيقات السكنية والتجارية والصناعية.
بفضل الشهادات العالمية الإضافية مثل SGS و RoHS و CE و IEC، فإن منتجات Ctube تلبي المعايير الدولية وتحظى بثقة كبيرة لمتانتها وسلامتها وجودتها طويلة الأمد.
شكراً لكم على القراءة. نأمل أن يكون هذا الدليل مفيداً، ونتمنى لكم التوفيق في مشروعكم.
لأي استفسارات تتعلق بالمشاريع أو للحصول على مزيد من المساعدة، يرجى الاتصال بنا.
الأسئلة الشائعة
س1: ما الفرق بين أنابيب التوصيل الكهربائي من النوع 40 وأنابيب السباكة من النوع 40؟
صُممت أنابيب التوصيل الكهربائية مقاس 40 لحماية الأسلاك. وهي مقاومة للأشعة فوق البنفسجية، ومثبطة للهب، ولها سطح داخلي أملس لتسهيل سحب الأسلاك. وتتوافق مع معايير السلامة الكهربائية.
تُستخدم أنابيب السباكة من النوع رقم 40 لنقل المياه أو السوائل. وهي تتميز بمقاومتها للضغط وتتوافق مع معايير السباكة.
حتى وإن بدت متشابهة، فهي مصنوعة لأغراض مختلفة ولا ينبغي استخدامها بشكل متبادل.
س2: ما هي الأدوات التي أحتاجها لقطع وتركيب أنابيب التوصيل الكهربائية من النوع رقم 40؟
شريط قياس – للحصول على طول دقيق.
قاطع أنابيب PVC أو منشار يدوي - لقطع الأنابيب.
أداة إزالة النتوءات أو سكين متعدد الاستخدامات - لتنعيم الحواف بعد القطع.
أداة ثني الأنابيب - إذا لزم الأمر لعمل ثنيات.
التركيبات - مثل الأكواع أو الوصلات أو المحولات.
مادة لاصقة مذيبة من مادة PVC - لربط الأنابيب والتجهيزات.
قلم تحديد – لتحديد مكان قص أو محاذاة الأجزاء.
س3: ما الفرق بين أنابيب PVC من النوع 40 وأنابيب المعدن الصلب (RMC)؟
مادة PVC من النوع رقم 40 هي مادة بلاستيكية خفيفة الوزن ومقاومة للتآكل وبأسعار معقولة. يسهل التعامل معها ولكنها توفر حماية مادية أقل.
تُصنع الأنابيب المعدنية الصلبة من الفولاذ أو الألومنيوم. وهي ثقيلة الوزن، وأكثر متانة، وتوفر حماية أفضل، ولكن تركيبها أصعب وتكلفتها أعلى.
اختر مادة PVC للأعمال الخفيفة أو الخارجية، ومادة RMC للمناطق الصناعية أو المناطق ذات التأثير العالي.