Table of Contents
Toggle1.Introduction
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) conduit is a popular material used for electrical installations due to its durability, flexibility, and ease of installation. It is made from a plastic polymer, which makes it lightweight yet strong enough to protect electrical wires from environmental damage.
When installing PVC conduit, achieving secure and reliable connections between conduit sections is crucial. The performance and longevity of the entire system depend heavily on how well the conduit is joined together. While PVC conduit itself is sturdy and dependable, the way it is connected—using the right connectors and adhesives—determines the integrity of the installation.
This post aims to provide a beginner-friendly explanation of PVC conduit glue, highlighting its importance in ensuring secure and durable installations.
2.Understanding PVC Conduit Glue
2.1 What Is PVC Conduit Glue?
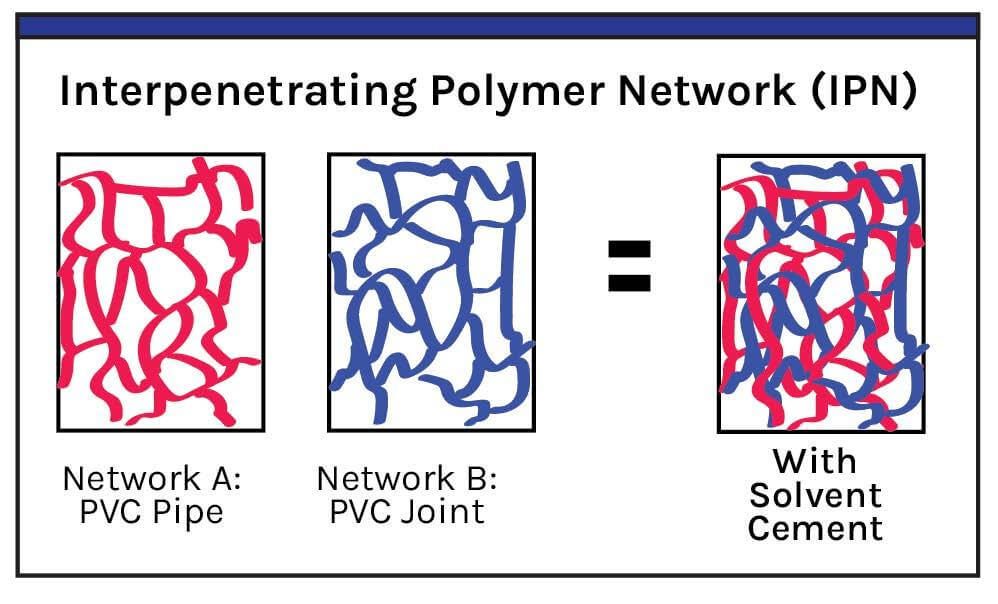
PVC conduit glue, also known as PVC cement or solvent cement, is a specialized adhesive used for bonding PVC pipes and fittings. Unlike regular adhesives, which rely on surface bonding, PVC conduit glue creates a chemical bond by softening and fusing the plastic surfaces.
The glue is typically made from a combination of solvents, resins, and stabilizers that work together to dissolve the outer layer of PVC. This allows the glue to penetrate the material, creating a molecular bond once it hardens. The result is a strong, durable, and leak-proof connection, ensuring the integrity of the conduit system.
The primary chemical components of PVC glue include:
- Solvents: These break down the PVC’s outer surface to enable the glue to fuse with the material.
- Resins: These help form a bond between the PVC pieces, ensuring strength and durability.
- Stabilizers: These control the viscosity and setting time of the adhesive, ensuring a smooth application.
PVC conduit glue is different from other types of adhesives (such as epoxy or rubber-based glues) because it creates a chemical reaction with PVC material, rather than merely adhering to the surface.
This unique bonding process makes it ideal for applications where a permanent, strong connection is required, such as electrical or plumbing installations.
2.2 How PVC Conduit Glue Works
PVC conduit glue works through a unique chemical bonding process. When the glue is applied to the surfaces of PVC conduit and fittings, the solvents in the adhesive begin to break down or “soften” the outer layer of the PVC. This allows the glue to penetrate deeper into the plastic, effectively creating a molecular bond between the two pieces.
- Surface Softening: The solvent in the glue dissolves the top layer of the PVC, softening the material. This is crucial because it allows the glue to penetrate the surface and bond with the PVC on a molecular level.
- Fusion: Once the glue is applied, the softened surfaces fuse together as the solvents evaporate. This process essentially “welds” the PVC conduit and fittings into one solid piece, forming a permanent, leak-proof bond.
- Curing: After the glue is applied and the pieces are joined, the adhesive begins to set as the solvent evaporates. This curing process typically takes a few minutes to a few hours, depending on the type of glue used. Full curing ensures the bond is strong and resilient.
- Strength and Durability: Once cured, the bond created by the PVC glue is extremely strong, ensuring that the conduit system is resistant to pressure, moisture, and temperature changes. This chemical bond is far more durable than a simple surface bond created by other types of adhesives.
3. Types of PVC conduit Glue
PVC conduit glue is essential for creating secure, long-lasting bonds between PVC pipes and fittings. The right adhesive ensures proper installation and functionality in electrical and plumbing systems. PVC glue is available in various types, each designed to meet specific application needs.
3.1 PVC Conduit Glue by Consistency
The consistency of PVC glue affects its ease of application, bonding strength, and suitability for different pipe sizes. The three primary types are:
- Regular Body PVC Glue: Regular body PVC glue has the thinnest viscosity, making it easy to apply and ideal for small-diameter pipes, usually up to 2 inches. Its lightweight consistency allows for quick application and is well-suited for non-pressurized systems or projects requiring less adhesive strength. This type of glue is commonly used in residential applications where the demand for high bonding strength is lower.
- Medium Body PVC Glue: Medium body glue has a balanced viscosity, making it versatile and easy to apply. It’s commonly used for standard PVC conduit pipes, typically ranging from 1 to 4 inches in diameter. Medium body glue provides a strong bond and is ideal for most residential and commercial applications.
- Heavy Body PVC Glue: Thicker than medium body glue, heavy body adhesive is designed for larger pipes (often 3 to 6 inches or above). Its thick consistency is especially useful for vertical or overhead installations, preventing dripping while ensuring a strong, durable bond. Heavy body glue is commonly used in industrial systems and larger plumbing or electrical applications.
- Extra Heavy Body PVC Glue: The thickest option, extra heavy body PVC glue is made for large-diameter pipes, typically 6 inches or more. It provides maximum control during application and forms a powerful bond, making it suitable for high-pressure or high-traffic systems. This glue ensures the adhesive stays in place during application and delivers the strongest seal for demanding environments.
Please check with the supplier for the dimensions of the applicable tubes for these different specifications to ensure proper application.
3.2 PVC Conduit Glue by Setting Time
- Slow Set Cement: Slow set cement is perfect for large-scale installations where extra time is needed to align pipes and fittings. It provides more working time before it begins to set, allowing for adjustments during the installation process. Ideal for complex setups, this type of cement is commonly used in installations where precision and careful handling are key.
- Medium Set Cement: Medium set cement is the most commonly used in standard installations. It offers a balance between work time and curing time, providing a good window for adjustments without taking too long to set. This cement is perfect for typical PVC conduit systems and offers strong bonding in a reasonable amount of time.
- Fast Set Cement: Fast set cement is designed for situations where time is critical. It starts setting quickly, usually within minutes, which can be advantageous for projects where speed is essential. It’s commonly used in smaller, straightforward installations where minimal adjustments are required and you need to move quickly.
- Extreme Fast Set Cement: Extreme fast set cement is perfect for situations where rapid curing is needed, such as in emergency repairs or installations that need to be completed in a very short timeframe. This type of cement sets in just seconds, making it ideal for fast-paced work but requiring precise application.
3.3 PVC Conduit Glue by Material Compatibility
PVC adhesives are also formulated to work with specific types of PVC, ensuring a strong bond with the material of the pipe. Here are the main types based on material compatibility:
- Standard PVC Glue: This is the most common type of adhesive and is designed for use with rigid PVC conduit and fittings. It is suitable for general-purpose plumbing and electrical installations, providing a secure bond for everyday use in most standard pipes.
- uPVC Glue (Unplasticized PVC): Formulated for uPVC pipes, which are rigid and used in applications requiring greater strength and resistance to environmental factors, uPVC glue is ideal for outdoor applications or pressure systems. It provides a high-strength bond to withstand temperature fluctuations and chemical exposure.
- CPVC Glue (Chlorinated PVC): CPVC glue is specially formulated for CPVC pipes, which are designed for hot water systems. It is resistant to higher temperatures and chemicals, making it ideal for industrial and high-temperature applications. CPVC glue offers excellent performance in plumbing and fire sprinkler systems.
3.4 PVC Conduit Glue by Color
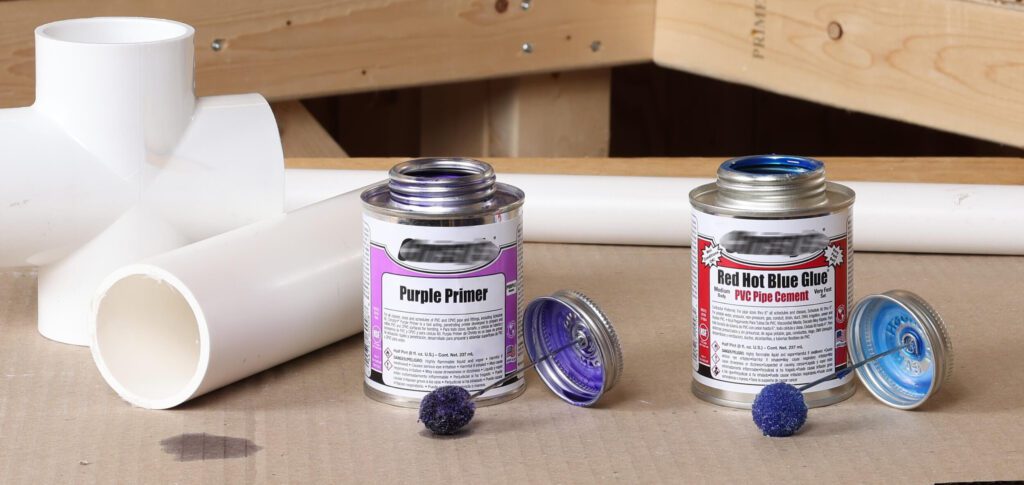
The color of primers and cements is intentionally designed to help building inspectors easily confirm that the correct products were applied during installation. ABS cement is commonly black but may also appear milky white. PVC cement is available in clear, gray, or blue varieties, with the blue version often used in non-pressure applications where a primer isn’t required. CPVC cement typically comes in yellow or orange, depending on the pipe brand.
Inspectors are trained to look for purple primer on PVC and CPVC joints, as its use is mandatory in most cases (unlike ABS, which does not require a primer). However, clear primer can be an acceptable alternative in areas where it complies with local codes or in projects that are not subject to inspection.
When connecting ABS to PVC—frequently necessary for linking household drain, waste, and vent systems to municipal sewer lines—green transition cement must be used to ensure a secure bond.
The color of the glue helps identify its intended use and provides visual indicators for specific applications. Common colors include:
- Clear PVC Glue: Clear glue is designed for general use with standard PVC pipes. It provides a clean, aesthetically pleasing finish and is used in situations where the appearance of the adhesive is important. It forms a strong bond without leaving visible residue.
- Blue PVC Glue: Blue glue is commonly used for CPVC pipes or systems that require resistance to higher temperatures. It is used primarily in industrial and hot water systems where the adhesive’s color helps indicate the type of glue used.
- Grey PVC Glue: Grey PVC glue is specially formulated for bonding Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC pipes and conduits. It is commonly used for rigid PVC conduits and fittings, which are thicker and require a stronger bond.
- Purple PVC Glue: Often used as a primer, purple glue is applied to the pipe before gluing to prepare the surface for bonding. It’s commonly required by building codes and helps ensure the adhesive forms a strong, lasting bond. Purple glue is often used in areas where pipe connections are inspected.
4. Why PVC Conduit Glue Is Essential for Electrical Projects
4.1 Creating Strong, Permanent Bonds
The primary function of PVC conduit glue is to chemically bond PVC pipes and fittings together. When applied to the surfaces of the conduit, the glue dissolves the outer layer of PVC, and once joined, the pieces fuse into one solid unit as it cures. This process is known as solvent welding. The result is a bond stronger than the material itself, ensuring that your conduit connections won’t separate, even under pressure or stress.
A strong, permanent bond is vital for maintaining the integrity of the entire conduit system, preventing any accidental disconnections or separations that could cause electrical malfunctions or safety hazards.
4.2 Preventing Leaks, Dust, and Water Infiltration
PVC conduit glue forms a watertight and airtight seal between the connected conduit pieces. This is particularly important for both underground and above-ground installations where moisture or dust can infiltrate and damage the wiring inside.
Underground installations are exposed to water and soil. If joints aren’t properly sealed, they could allow moisture to seep into the conduit, leading to short circuits, corrosion, or damage to cables. PVC glue prevents this by creating a secure, sealed environment.
Above-ground installations are vulnerable to external elements like rain, snow, and debris. Without glue, these elements could cause the conduit to degrade over time or cause electrical faults.
By using PVC glue, you are ensuring that your electrical system remains protected from the elements.
4.3 Improving Structural Integrity
In addition to sealing and bonding, PVC conduit glue enhances the overall structural strength of the conduit system. When joints are glued, the PVC conduit becomes more resistant to physical stresses, such as impact, pressure, or vibrations. This is especially important in environments where the conduit might be subjected to external forces—like in industrial settings or areas with heavy machinery.
PVC is lightweight but also durable when installed properly. Using glue helps the conduit withstand bumps, vibrations, or any other physical stresses that could otherwise cause cracks or breakage at the joints.
4.4 Compliance with Safety Standards
In most countries, including the U.S., electrical codes like the National Electrical Code (NEC) require that all electrical conduit systems be securely joined using appropriate materials, including PVC conduit glue. Failure to use the proper adhesive could lead to violations of these codes, which may result in:
- Safety risks: Loose joints can compromise the safety of your electrical system, leading to electrical shorts, fires, or exposure to harmful conditions.
- Legal repercussions: Non-compliance with local regulations can lead to fines, the need for costly rework, or even the invalidation of an installation, especially for commercial projects.
By using the right PVC glue, you ensure that your installation is code-compliant, safeguarding both the system and your project from legal and safety issues.
4.5 Ease of Installation
One of the most significant advantages of using PVC conduit glue is its ease of use. Unlike mechanical fittings that require additional tools, labor, or complex installation methods, PVC glue simplifies the process:
- Quick application: Applying glue is a fast and straightforward process—just a few seconds to apply the solvent cement to the joint, then press the pieces together for a secure connection.
- No need for specialized tools: Unlike some metal conduit systems that require welding or threading, PVC conduit only needs a small brush or applicator to apply glue, making it a more accessible solution for DIYers or professionals alike.
This efficiency not only saves time but also reduces labor costs and the overall complexity of the installation.
4.6 Cost-Effectiveness
PVC conduit glue is also highly cost-effective. It provides a durable, secure bond without the need for more expensive joining methods like welding or using threaded metal fittings. This makes PVC glue a great option for both large-scale and small-scale electrical installations.
Compared to other materials, solvent cement is inexpensive, and a single canister can bond many joints, reducing costs significantly.
The affordability of PVC conduit glue makes it ideal for both residential and commercial electrical installations.
4.7 Long-Lasting Durability
Once applied and allowed to cure, PVC conduit glue creates an extremely long-lasting bond that won’t break down over time. Unlike some other adhesives, PVC glue is resistant to environmental factors like heat, moisture, and UV rays. This makes it ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications, ensuring your conduit system remains intact for many years without needing maintenance or repairs.
In outdoor installations, this durability is essential, as the glue ensures that the conduit remains securely in place, even under harsh weather conditions.
4.8 Versatility for Different Applications
PVC conduit glue is compatible with a variety of PVC conduit types and sizes. Whether you are working with schedule 40, schedule 80, or other PVC conduit options, there is a solvent cement specifically designed to work with these materials.
This versatility means that no matter what your installation requires—be it electrical, telecommunications, or other low-voltage systems—PVC conduit glue is a go-to solution that ensures reliable and secure connections across various applications.
5. How to Choose the Right PVC Conduit Glue?
When working with PVC conduits, selecting the correct glue is essential for achieving a strong, leak-proof, and durable connection between your pipes and fittings. PVC glue (or PVC solvent cement) chemically bonds PVC materials together, ensuring long-lasting performance. Let’s dive deeper into how to choose the best PVC conduit glue for your installation:
5.1 Understand the Types of PVC Conduit
PVC conduit comes in various types, and it’s essential to know which one you’re working with to choose the right glue. The primary types of PVC conduits include:
- Schedule 40 PVC Conduit: This is the most common type used for residential and commercial electrical installations. It is thinner-walled than Schedule 80, so you’ll need a solvent cement suitable for this application.
- Schedule 80 PVC Conduit: Known for its thicker walls, Schedule 80 is used in applications requiring greater strength and durability, such as industrial or high-pressure environments. Schedule 80 pipes require a stronger cement for a solid bond.
- DB Series Conduit: For outdoor and underground installations, DB series conduits offer extra durability and UV resistance. A specialized adhesive that can withstand harsh environments is ideal for such systems.
Make sure the glue you choose is compatible with the type of conduit you are using. Always check the packaging for product compatibility.
5.2 Consider the Temperature and Environmental Conditions
PVC conduits and the glue used with them must withstand varying environmental conditions, especially temperature fluctuations. When selecting glue, consider the following:
- Temperature Resistance: Different solvent cements are designed to handle different temperature ranges. If you’re working in high-temperature environments (like attics or areas near heat sources), you’ll need a heat-resistant glue. For cold climates, make sure the glue can handle subzero temperatures without losing its bond strength.
- Outdoor Use and UV Resistance: If your installation will be exposed to sunlight, such as for outdoor wiring, choose a glue that offers UV resistance. Some glues come with added protection to prevent degradation from sun exposure.
5.3 Choose the Correct Glue Strength
PVC glues come in varying strengths depending on the application:
- Regular Strength: Ideal for smaller residential or light-duty commercial projects. If you’re working with standard Schedule 40 PVC for household electrical systems, regular strength glue will do the job.
- Heavy Duty Strength: Use heavy-duty solvent cements for industrial, high-pressure, or large-diameter pipe installations. These glues provide extra holding power and resistance to shock, chemicals, and extreme environmental conditions.
The glue strength is typically indicated on the label, and it’s important to select one that matches the size and demands of your conduit installation.
5.4 Viscosity and Ease of Application
PVC solvent cements come in different viscosities (thicknesses). The viscosity affects how easily the glue is applied and how well it fills gaps between conduit and fittings.
- Thin Cement: Easier to apply and flows more easily into tight spaces, making it suitable for smaller diameter pipes or delicate fittings.
- Thick Cement: More suited for larger pipes, heavy-duty applications, or when working in windy or outdoor conditions where thinner cements may evaporate too quickly. Thick cements also offer more control when applying to large joints or fittings.
For general household or light commercial applications, a medium-viscosity cement is often the best choice.
5.5 Primers and Two-Part Systems
Some PVC adhesives require a primer before application. Primer is used to clean and prepare the surfaces of the PVC and fittings, improving the bond strength. While primer is not always necessary for smaller jobs or certain types of PVC, it’s often recommended for high-stress or underground applications, as it ensures a cleaner, stronger bond.
Two-Part Systems: Some advanced systems require both a primer and a solvent cement for the strongest bond, especially for larger or thicker conduits. These systems are typically used in industrial-grade applications, but they can provide extra durability for heavy-duty systems.
6.Step-by-Step Guide on Applying PVC Conduit Glue
6.1 What You’ll Need
Before diving into the process, make sure you have all the necessary tools and materials. Having everything ready to go will ensure a smooth and efficient job:
- PVC conduit (the pipe you are connecting)
- PVC fittings (elbows, couplings, or connectors)
- PVC primer (optional but highly recommended for clean and secure joints)
- PVC solvent cement (also called glue)
- Brush or dauber applicator (usually included with solvent cement)
- Utility knife or pipe cutter (for clean cuts)
- Cleaning cloth (to remove dirt and debris)
- Gloves and safety goggles (for protection against fumes and splashes)
6.2 How To Cement PVC Conduit for Electrical Wiring
The process of preparing and bonding PVC conduit and fittings involves several key steps to ensure a strong, durable connection.
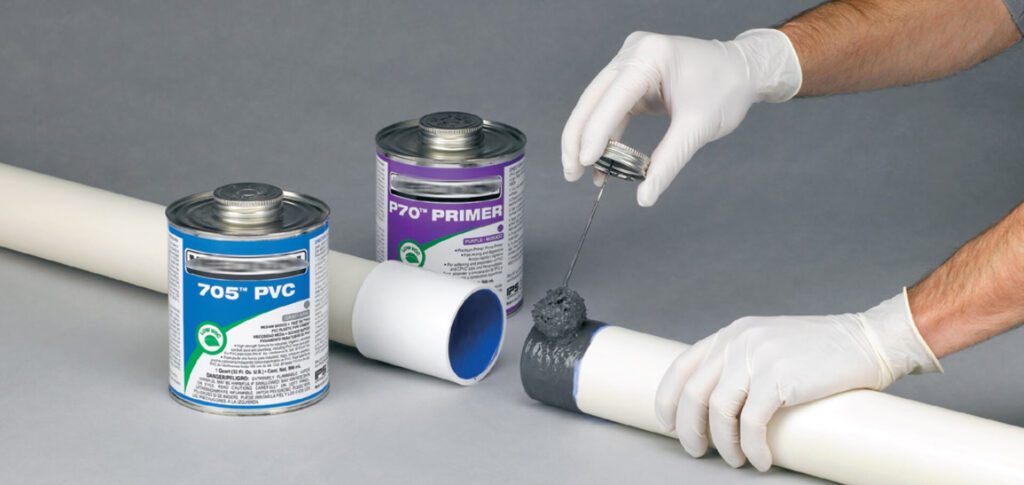
First, clean the conduit and fittings to remove dirt, dust, and grease, and make clean cuts if necessary. Dry-fit the pieces together to check the fit before applying any glue. While optional, applying PVC primer is recommended to enhance the bond, especially for larger or outdoor installations.
After priming, apply an even coat of PVC solvent cement to both the conduit and fitting, and quickly assemble the pieces, holding them together for 10-30 seconds to ensure a strong bond.
Wipe off any excess cement to prevent a messy joint and allow the connection to cure for at least 15 minutes. Finally, test the joint for stability after the cement has fully cured, ensuring the bond is secure.
We make a detailed guideline in the following for reference.
Step 1: Preparing the PVC Surfaces
To create the strongest bond, both the conduit and the fittings must be properly prepared. Dirt, dust, grease, or moisture can weaken the bond and cause leaks over time. Here’s how to prepare the surfaces:
- Clean the Conduit and Fittings: Use a rag to wipe the ends of the conduit and the inside of the fitting to remove any dirt, dust, or grease. For a smoother finish, you may use a PVC pipe cleaner.
- Cut the Conduit: If you’re cutting PVC conduit to size, use a utility knife or pipe cutter for clean, straight cuts. A rag or cloth can also be used to wipe off any plastic shavings from the cut ends.
Step 2: Dry-Fit the Pieces
Before applying any glue, it’s important to dry-fit the pieces together. This means assembling the conduit and fittings without glue to check for a proper fit.
Step 3: Applying PVC Primer (Optional but Recommended)
Although applying PVC primer is optional, it is strongly recommended, especially for outdoor installations or larger conduit systems. The primer works by cleaning and softening the PVC surfaces, making the glue bond stronger and more effective.
- Apply the Primer: Use a clean applicator brush or dauber to apply a thin coat of PVC primer to both the outside of the conduit and the inside of the fitting. Be sure to cover the entire bonding surface.
- Allow the Primer to Dry: Wait for a few seconds (but not too long—refer to the primer manufacturer’s instructions). The primer should be tacky but not wet before you proceed.
Step 4: Apply PVC Solvent Cement (Glue)
PVC solvent cement is what bonds the PVC pieces together. It works by chemically softening the surfaces of the PVC and allowing them to fuse together as the cement cures.
- Use the Correct Cement: Make sure you’re using the right solvent cement for the type and size of PVC conduit you’re working with. Different types of cement are made for different pipe diameters and applications.
- Apply an Even Coat: Using the applicator brush or dauber, apply an even coat of solvent cement to both the outside of the conduit and the inside of the fitting. Be sure to coat the entire area that will be joined—this helps ensure a uniform, strong bond.
- Don’t Overapply: While it’s essential to apply enough cement to cover the surfaces, avoid excess glue, as it can cause a messy, unattractive joint and make the curing process longer.
Step 5: Assemble the Pieces Quickly
Time is of the essence once the cement is applied. PVC solvent cement starts setting rapidly, so you must join the conduit and fitting right away:
- Join the Pieces: Align the conduit and fitting carefully, then push them together firmly. A slight twisting motion helps spread the cement evenly.
- Hold the Joint Together: Once the pieces are connected, hold them in place for 10-30 seconds to ensure the bond sets before releasing. The glue will start to hold almost immediately, but holding the joint ensures proper adhesion.
Step 6: Wipe Off Excess Cement
Once the conduit and fitting are connected, use a clean rag to wipe away any excess cement. This step is important because:
Excess glue can drip or create a mess around the joint. Any leftover solvent cement could interfere with the curing process and leave a sticky residue on the outside of the conduit.
Step 7: Let the Cement Cure
After the joint is glued and excess cement is wiped away, the joint needs time to cure. Curing time will depend on factors such as:
- Temperature: Higher temperatures accelerate the curing process.
- Humidity: Moisture can sometimes affect the bonding process.
- Type of Cement: Different cements may require different curing times.
As a general rule, allow the cement to cure for at least 15 minutes before handling the assembly. For a fully hardened joint, let it cure for several hours or as per the cement manufacturer’s instructions.
Step 8: Test the Connection
Once the cement has fully cured, test the connection by gently pulling or twisting the conduit. The joint should feel solid, with no movement or signs of loosening. If there is any movement, it may indicate that the bond wasn’t properly formed, and you may need to reapply the glue.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
Not Cleaning the Surfaces: Failing to remove dirt or moisture from the surfaces can lead to a weak bond.
Not Using Primer: Skipping the primer can result in a less secure connection, especially on larger pipes or outdoor installations.
Applying Too Much Glue: Overapplying cement can lead to drips, an uneven bond, and longer curing times.
Not Working Quickly Enough: PVC solvent cement sets quickly, so it’s essential to assemble the pieces soon after applying the glue.
Skipping the Cure Time: Rushing the curing process may result in a weak bond, so give it enough time to fully set.
7. Conclusion
In this guide, we’ve explored the essential role that PVC conduit glue plays in ensuring secure and long-lasting connections between PVC conduits and fittings.
From understanding the composition and types of PVC glue to recognizing the significance of color codes for different applications, we’ve highlighted how choosing the right adhesive can prevent leaks, improve durability, and enhance system performance.
The proper technique for applying PVC conduit glue — including surface preparation, correct application amounts, and allowing adequate curing time — is critical for achieving a strong and effective bond.
When it comes to electrical installations, the choice of every component is crucial, whether it’s the glue or the conduit itself.
Ctube is a specialized supplier of high-quality PVC conduit solutions, including our special series UPVC Solar Conduit, Low Smoke Halogen-Free Conduit, and a variety of other products tailored to meet the needs of electrical installations. Our conduits come in multiple specifications and certifications, ensuring that they meet the highest standards of durability, performance, and safety.
Whether you’re working on a residential, commercial, or industrial project, Ctube has the right conduit solution for you.
FAQs
1. How do I separate a joint that has been cemented together and cured?
Once a PVC joint is cemented and cured, it is difficult to separate. If necessary, you can try using a pipe cutter or saw to cut through the conduit and remove the fittings. In some cases, a heat gun may soften the glue, but this is generally not recommended as it could damage the pipe or fitting.
2.How long does PVC glue take to dry?
PVC glue typically dries to the touch within 10 minutes, but full curing can take 24 hours. For a strong bond, it’s best to allow the glue to cure for the recommended time before putting the conduit into service.
3.Can PVC glue be used on wet surfaces?
PVC glue should not be used on wet surfaces, as it can prevent the adhesive from bonding properly. For best results, ensure the surfaces are clean and dry before applying the glue. Some specialized PVC adhesives are designed for damp conditions, so check the product label for specific instructions.