1. Introduction
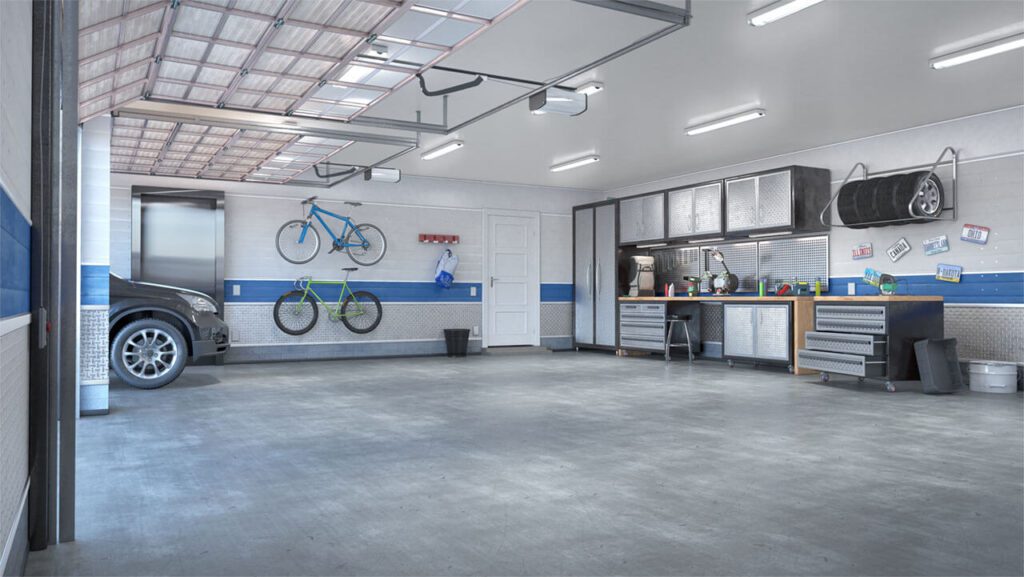
To choose metal or PVC conduit, it is a question. Imagine you are standing in your finished garage and want to install some new outlets. You are considering using metal conduit, but you’ve never used it before and think it’s a pain in the ass to get it bended. And you want to use PVC conduit instead, but don’t think it’s strong enough in the garage. Really a conundrum, isn’t it?
This time if you know enough about PVC, RMC, EMT and IMC, solving this problem will be a piece of cake for you. In the field of electrical conduit, you can choose from many materials and brands. In this post, we will explain all the commonly used types and elaborate on the advantages and disadvantages of each material.
2. What is PVC conduits and metal conduits?
PVC stands for Polyvinylchloride which is a tenacious chemically resistant synthetic resin. It has been a widely used plastic material to protect power in houses, telecommunications and utilities since 1932. A PVC conduit is commonly known as a white rigid (or flexible) PVC tube for threading and protecting wires from corrosion and electrical leakage.
The most basic of the home improving is the installation of wire layout. In order to protect the wire when designing the system, we will use PVC conduit. Since the wire thickness is different, PVC conduit is also divided into different size specifications to adapt to the arrangement.
PVC conduit stops burning and electrical leak, resists corrosion, moisture and sunlight, so it is especially suitable for outdoor projects where it is used to protect wires and workers.
Metal conduit is also created to protect electrical wires and cables. It is commonly used to run along building walls and floors, but due to its durability, it is also suitable for exposed areas that are susceptible to impact. Metal conduit can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it a good choice for hazardous site conditions in industrial and commercial applications. They are classified as RMC, EMT, IMC and FMC. The RMC and IMC metal conduits are more pressure-bearing than others and are suitable for heavy-duty applications where physical damage is more likely to occur. EMT conduits are easier to bend and cut so they help create smooth and continuous run for faster wire installations.
3. What are the different types of conduits?
There are 7 different types of conduits used commonly in residential and light commercial wiring.
3.1 RMC – Rigid Metal Conduit
Rigid Metal Conduit, a threaded rigid raceway with a circular cross section and thick walls. One of the main advantages of the RMC is that its thick walls protect sensitive equipment from electromagnetic interference. The difference between the RMC and the EMT is that the EMT is not threaded, while the RMC is threaded and has thicker and heavier walls, thus costing more.
The material of this type of metal conduit is generally steel which is divided into galvanized and non-galvanized steel. The galvanizing process adds a protective layer of zinc to steel conduit to help prevent corrosion. This type of RMC is called GRC (galvanized rigid conduit). Even so, however, GRC is still susceptible to rust and deterioration.
Steel is difficult to escape from corrosion. But aluminum can resist it except some extreme corrosive environments like the earth. In addition to steel, aluminum conduit is an important class of metal conduits. Aluminum does not allow electromagnetic interference (EMI) to damage sensitive equipment. The wiring inside the conduit sometimes generates electromagnetic interference, but aluminum prevents this from happening.
Steel is essentially 250% times denser than aluminum, making it obviously heavier. And due to its high density/weight, it’s less likely to bend under force or heat. As a result, it will cost less to buy and ship aluminum conduits. You can also save on labor costs. Since a 20-foot-long aluminum conduit weighs less than 80 pounds, two workers can easily complete the installation. You’d need to assign four workers to install the same length of steel, since it weighs about 200 pounds.
3.2 EMT – Electrical Metallic Tubing
Electrical Metallic Tubing, a thin-walled rigid metal tubing without threads. It is often used in place of galvanized rigid conduit (GRC), and made of coated steel or aluminum. This conduit type does not provide the same protective strength as RMC, but is lighter. 2 EMTs can be connected with a connector fitting and screws are not needed. EMTs are lighter in weight and less expensive than both RMC and GRC.
Essentially, EMT is a raceway for you to pass wires through. You can run it down a wall exposed or it can be concealed behind walls or put in concrete or direct buried into the earth. Of course you have to have specific kinds that can handle that. The earth is very corrosive to metals so you need to have either a stainless or galvanized to be able to do that. If you are going to use regular aluminum EMT that stuff overtime is going to corrode. And finally the corrosion makes the tubing break and ruined.
3.3 IMC – Intermediate Metal Conduit
Intermediate metal conduit is a rigid metal electrical conduit designed for outdoor exposure and secure connections. It is specifically designed to protect insulated electrical conductors and cables. It is two-thirds the weight of RMC. You can use IMC anywhere a thin-walled conduit is allowed.
IMC conduit is coated externally with a hot-dipped galvanized coating and internally with a special corrosion-resistant coating to extend the life of the conduit. The common conduit sizes are ranging from 1/2″ to 4″ in diameter. IMC was originally introduced by Allied Tube & Conduit and is manufactured to meet UL (formerly Underwriters Laboratories) Safety Standard 1242 and ANSI C80.6. The National Electrical Code (NEC) includes a specific provision detailing the proper use of IMC, Article 342. IMC conduit is connected with threaded fittings to ensure a safe and secure joint. Installation usually takes large pliers or a pipe wrench.
In addition to being lighter in weight, IMC has a larger inside diameter than RMC, and the smoother interior of the conduit makes it easier to pull wires through the conduit. On the other hand, The National Electrical Code permits the use of IMC in all of the same applications RMC is approved for. That’s why IMC has replaced RMC in many applications, including residential and commercial.
In terms of weight, IMC falls between RMC and EMT, which is typically used for branch circuit wiring in homes and commercial buildings. Unlike IMCs, EMTs are never threaded and are not designed for solid joints like IMCs and RMCs. IMC usage is typically restricted to service entrance components and exposed runs to and from exterior service panels.
3.4 FMC – Flexible Metal Conduit
Flexible metal pipe (FMC) is also known as “Greenfield”, after its inventor. It has a spiral structure that gives it flexibility so it can snake through walls and other structures. Standard FMC is used for dry indoor locations and is commonly used for short runs between wall boxes and motors or stationary equipment such as garbage disposals.
3.5 ENT – Electrical Non-metallic Tubing
Electrical non-metallic tubing is flexible corrugated plastic tubing that is moisture resistant and flame retardant. It is easily bent and installed with snap-lock or glued plastic fittings. Unlike EMT, non-metallic conduit (usually PVC corrugated conduit) cannot be installed in exposed locations, so it is typically available for walls, floors and permanent or drop-in (free air only) ceilings. In addition to installation in standard wood or metal framed walls, ENT can also be installed in concrete block construction and can be covered with concrete.
ENT is lightweight, hand-bendable and has no sharp edges which reduces installation time and saves money. Because of the blue color of a common brand of this conduit, ENT is nicknamed “Smurf pipe,” taken from the Smurf cartoon character.
3.6 Rigid PVC Conduit
Rigid PVC Conduit, as the name implies, is a rigid PVC raceway suitable for direct burial in the ground for many applications. Ctube offers a complete line of rigid PVC conduit and fittings. For commercial, industrial and utility use, Ctube PVC conduit is proven to be durable and effective for years of maintenance-free performance in underground, sealed and exposed applications that meet the National Electrical Code. Our rigid PVC electrical conduits are:
- Commercial, industrial, utility and home use
- Not galvanic and magnetic
- Moisture and corrosion resistant
- Self-extinguishing and fire resistant
- Robust and impact resistant
- Waterproof
- Not aging under the sunlight
If you’re interested in Ctube’s rigid conduits and corrugated conduits, please feel free to contact us and inquiry.
3.7 PVC Coated Conduit
PVC coated conduit is the best combination of metal and PVC conduit. After galvanizing and threading the original steel conduits, people coat them with polyurethane and PVC. This way you get both the benefits of metal (strength, weight, durability, grounding) and the benefits of PVC (rust and corrosion resistance). PVC coated conduit is designed to get a compromise solution for long-lasting and corrosion-free electrical conduit systems.
| Category | PVC Conduits | Metal Conduits |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), lightweight and flexible. | Galvanized steel, aluminum, or stainless steel; rigid and mechanically strong. |
| Corrosion Resistance | ✅ Excellent (ideal for humid/chemical environments, e.g., coastal/industrial areas). | ❌ Requires coatings to resist rust (stainless steel performs better). |
| Fire Resistance | ❌ Softens under high heat; not suitable for fire-rated systems (unless flame-retardant additives are used). | ✅ Steel/aluminum withstands high temperatures; ideal for fire safety zones. |
| Electrical Conductivity | ✅ Non-conductive, no electromagnetic interference (EMI); ideal for data/telecom lines. | ❌ Conducts electricity; requires grounding. May cause EMI if unshielded. |
| Weight | ✅ Lightweight (~1.4g/cm³), easy to transport and install. | ❌ Heavy (steel: ~7.8g/cm³), requires additional structural support. |
| Installation | ✅ Easy to cut and bend (cold-forming); minimal tools required. | ❌ Requires specialized tools (e.g., conduit benders, threaders). |
| Cost | ✅ Lower material and labor costs (~1/3 the price of steel). | ❌ Higher material and installation costs (stainless steel is most expensive). |
| Temperature Tolerance | ❌ Brittle in extreme cold (<-5°C); deforms in high heat (>60°C). | ✅ Steel handles -40°C to 200°C; suitable for harsh environments. |
| Impact Resistance | ❌ Moderate (thick-walled PVC improves durability). | ✅ High resistance to crushing/impact; ideal for industrial settings. |
| Lifespan | ✅ 20–50 years (if UV-protected). | ✅ 30–70 years (galvanized steel with intact coating). |
| Environmental Impact | ❌ Contains chlorine; releases toxins if burned. Recyclable. | ✅ Steel/aluminum are 100% recyclable and eco-friendly. |
| Certifications | UL 651 (US/Canada), IEC 61386 (global), BS EN 61386 (EU). | UL 6 (steel), UL 4 (aluminum), NEMA RN-1 (industrial). |
4. How to choose and where are they used?
Above we have listed the different material types of conduits and briefly introduced their characteristics. Now we have an over-all summary of common pros and cons of metal conduit and PVC conduit.
4.1 Pros of metal conduit
- Excellent structural strength, extrusion resistance and impact resistance
- Electrically conductive
- High temperature resistance
- UV resistant
- Bite resistant (refers to animals)
- resistant to insect and microbic attack
- Waterproof
- Anti-explosion
- Resistant to EMF and RF noise
4.2 Cons of metal conduit
- High thermal conductivity
- Electrically conductive
- Vulnerable to corrosion damage
- Vulnerable to kinking
- Requires special tools for bending
- High cost
4.3 Pros of PVC conduit
- Anti-corrosion
- Low thermal conductivity
- Electrically insulated
- Easy to bend and install
- Flexible or semi-flexible
- Waterproof
- Explosion-proof
- Insect resistant
- Low cost
4.4 Cons of PVC conduit
- Not resistant to high temperature
- Electrically insulated
- Vulnerable to bite (refers to animals)
- Vulnerable to microbial attack
- Lower structural strength than metal conduit
It is important to note that conductivity can be both an advantage and a disadvantage depending on the application. Therefore, there is no one-size-fits-all choice in a conduit application guide. Each application must be designed according to those materials that are best suited for it. It is also common to use a mix of materials in the same application as parameters change at different points in the operation. For example, PVC conduit can be used for the earth and then switched to rigid steel or aluminum conduit where the conduit system is exposed to livestock. Similarly, a rigid metal conduit may be run inside a rigid PVC conduit where both the high structural strength and corrosion protection are needed. Sometimes a compromise is made by using PVC coated conduit.
Now let’s go back to the question at the beginning of the post: How do you choose conduit in your garage?
A more professional choice is to choose EMT and pull a ground wire. Because it is an indoor application and EMT is tough enough. Normally PVC will shred, EMT will develop a slight oval shape, and RMC will leave dents in your forklift. While not easy for the inexperienced, an EMT that is easy to bend is a better choice. Single bends are simple and small offset S-bends can be easily mastered. Of course PVC is way easier to pull but it would not even be a factor into the equation in a residential garage. If you want to save from bending too much, try to run the EMT high horizontally and set a few drops of conduit. This plan saves your wall space and keep conduits clean.
And it solves the problem of grounding wires for you. That’s an aesthetic choice. PVC is great if you bury it underground. But in this garage job, you might make a terrible and unsightly conduit run. Why not use RMC?It is very tough, but not cost-effective. Never go for it unless you need to hit the conduit with a heavy-duty forklift.
5. Conclusion
This is our complete guide to help you choose from metal conduit and pvc conduit.
Electricity is essential in the modern world. Any residential or commercial building must ensure that the electrical system is stable. Electric wires are made for this purpose. Since the wires cannot run on the building, conduits are installed on the surface and inside of the walls through which these wires are led to the service point. The secondary function of the conduit is to maintain the aesthetics of the building and to protect the wires from any external hazards. In essence, therefore, the structure of the project, the environment, and the size and weight of the wires determine the size and type of electrical conduit and fittings required.
In the late 19th century, many fixtures were converted from gas to electric. Wires were threaded directly into old gas pipes, creating some of the earliest examples of conduit. Nowadays conduit styles range from fairly sturdy construction to extremely tough conduit that you can drive through without damaging it.
We hope this post will help you to look at your choices from multiple perspectives. You may start from here and may have to choose conduit that both meets your needs and fits the standard like National Electrical Code in the future. You finally dive into the electrical industry no matter you are on a utility project management or doing your home improvement.
“If one tries to think about history, it seems to me – it’s like looking at a range of mountains. And the first time you see them, they look one way. But then time changes, the pattern of light shifts. Maybe you’ve moved slightly, your perspective has changed. The mountains are the same, but they look very different.”
Robert Harris